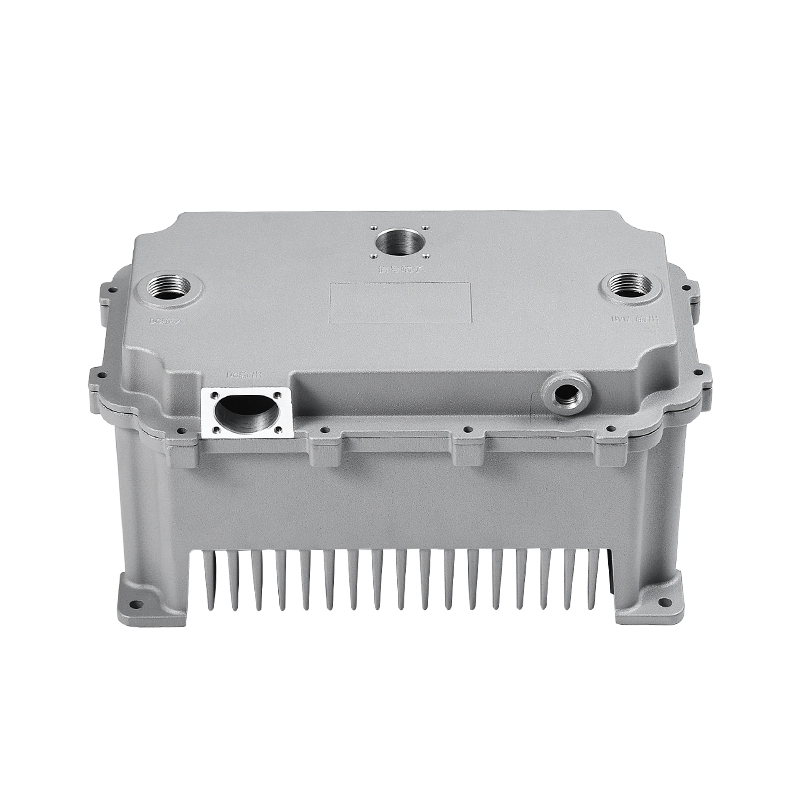
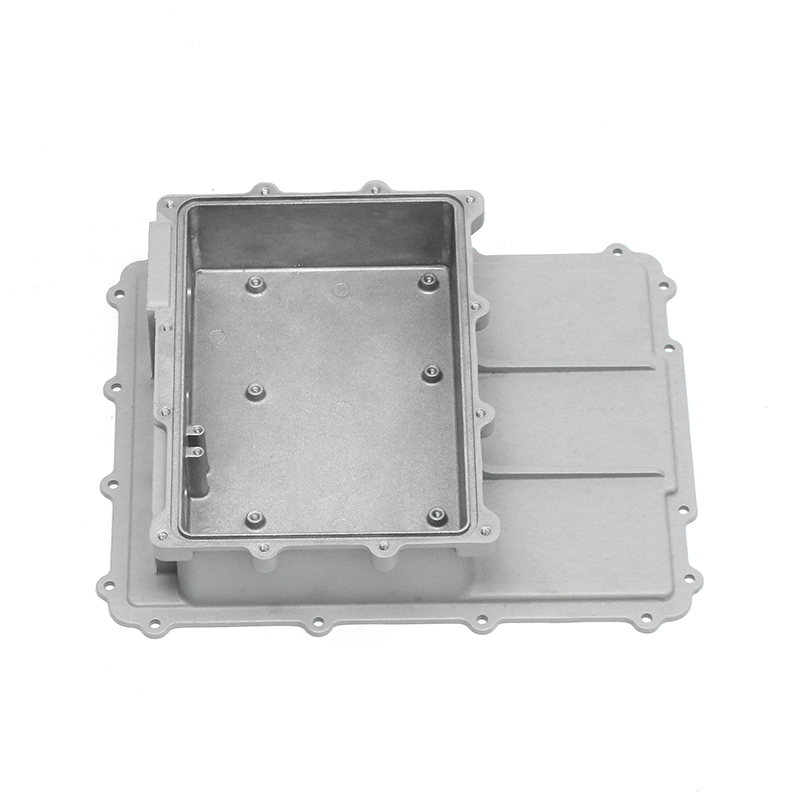
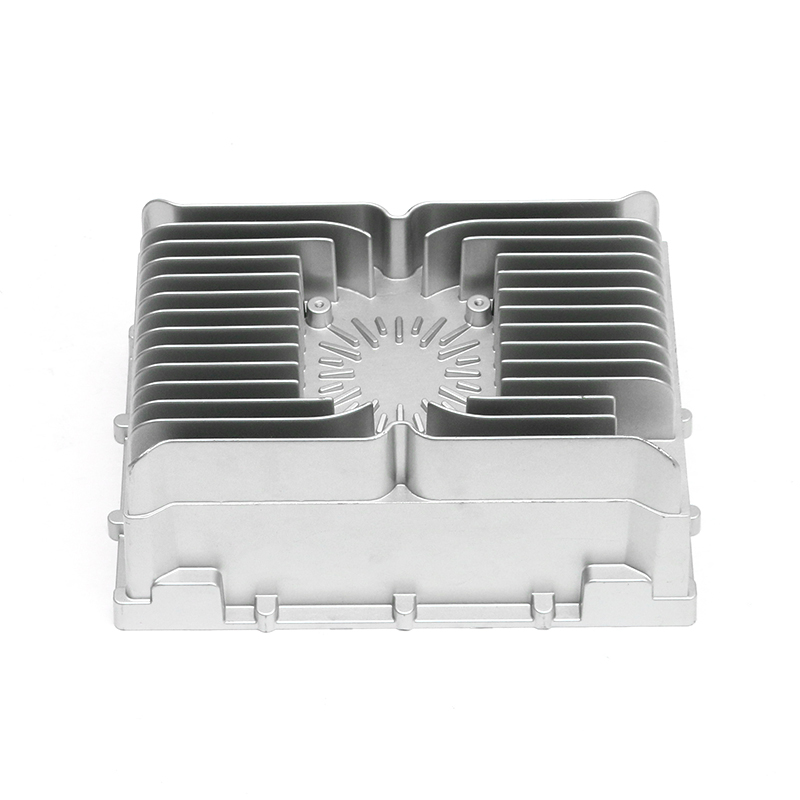
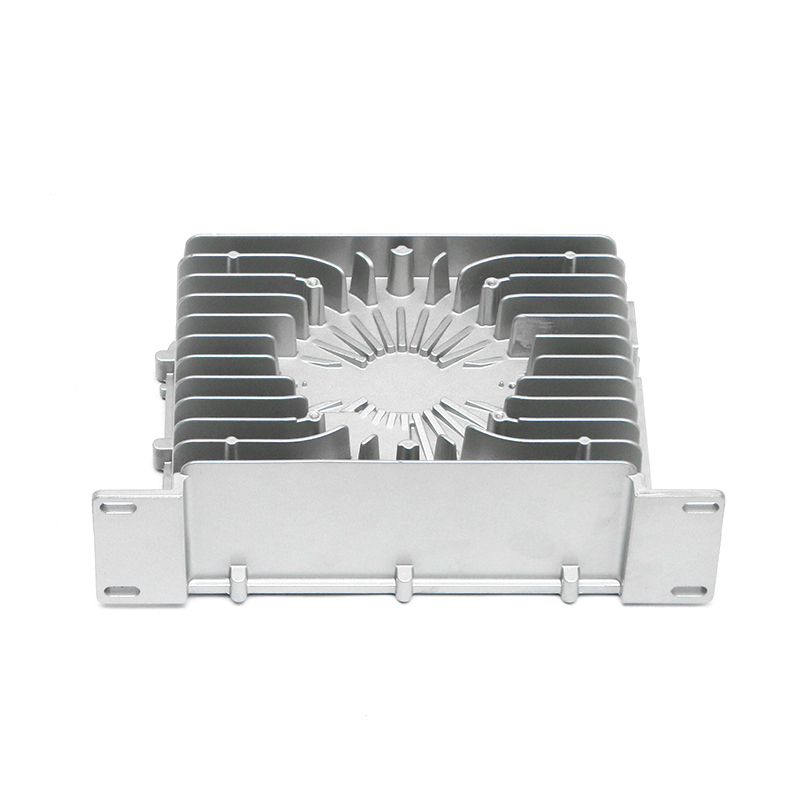
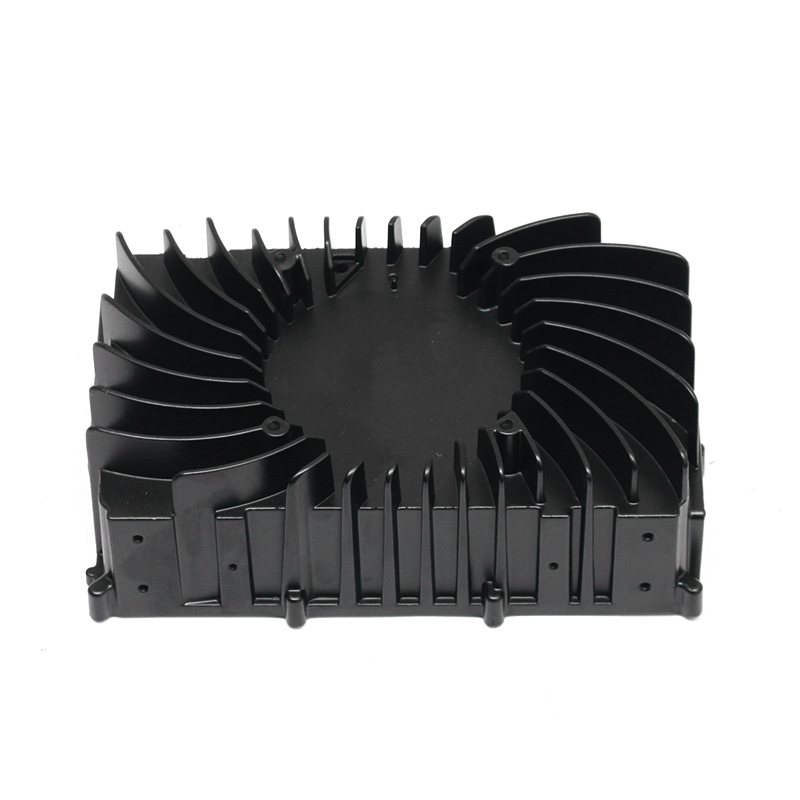
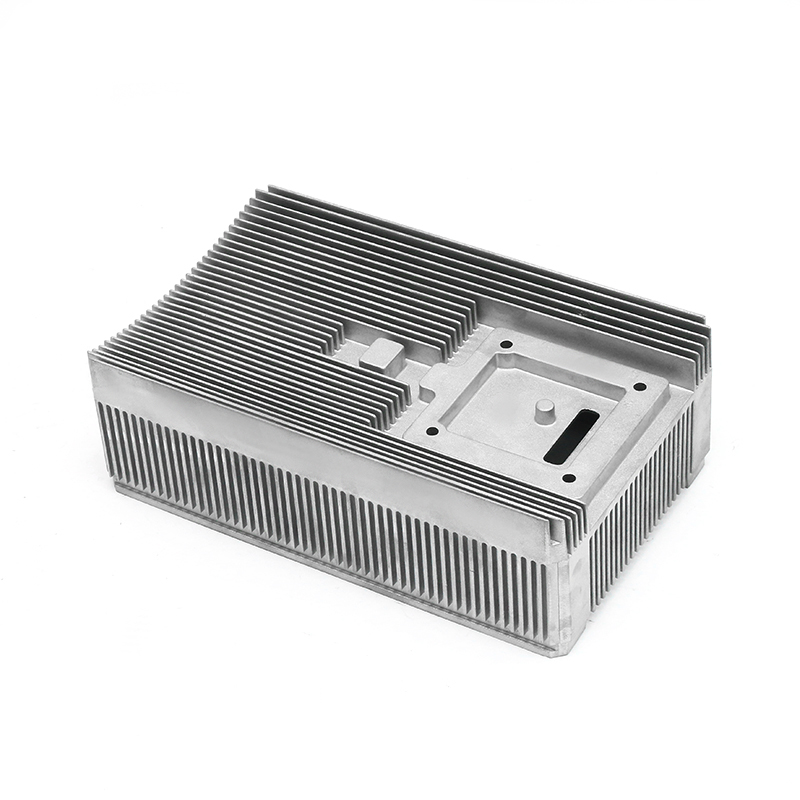
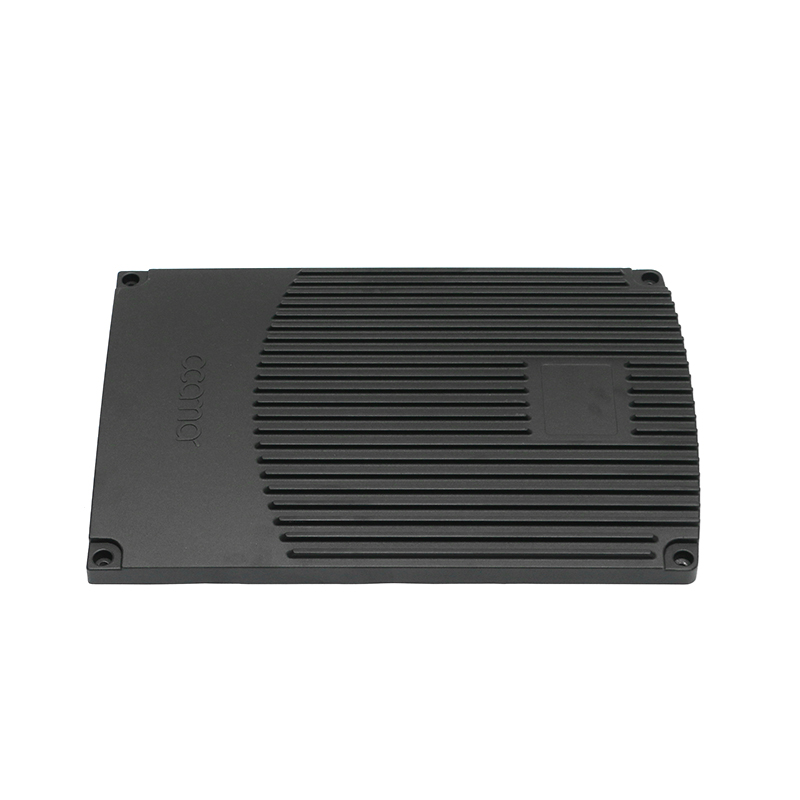
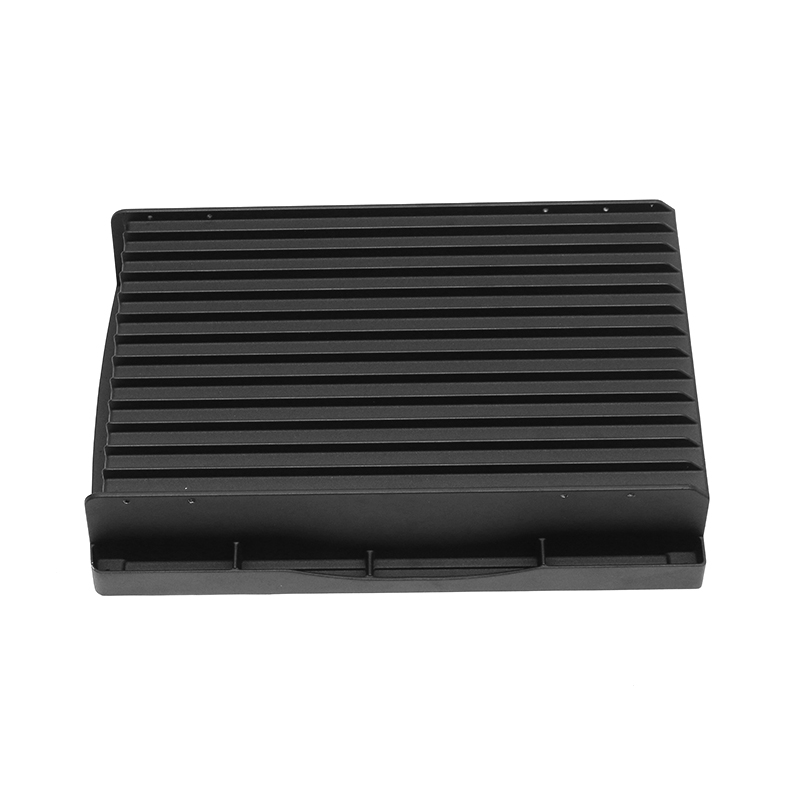
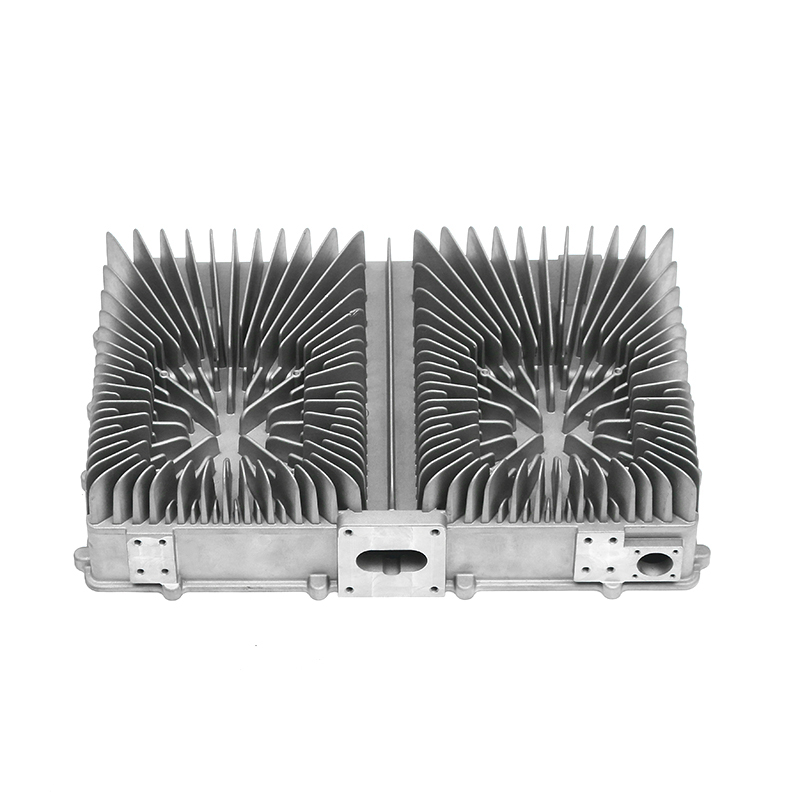
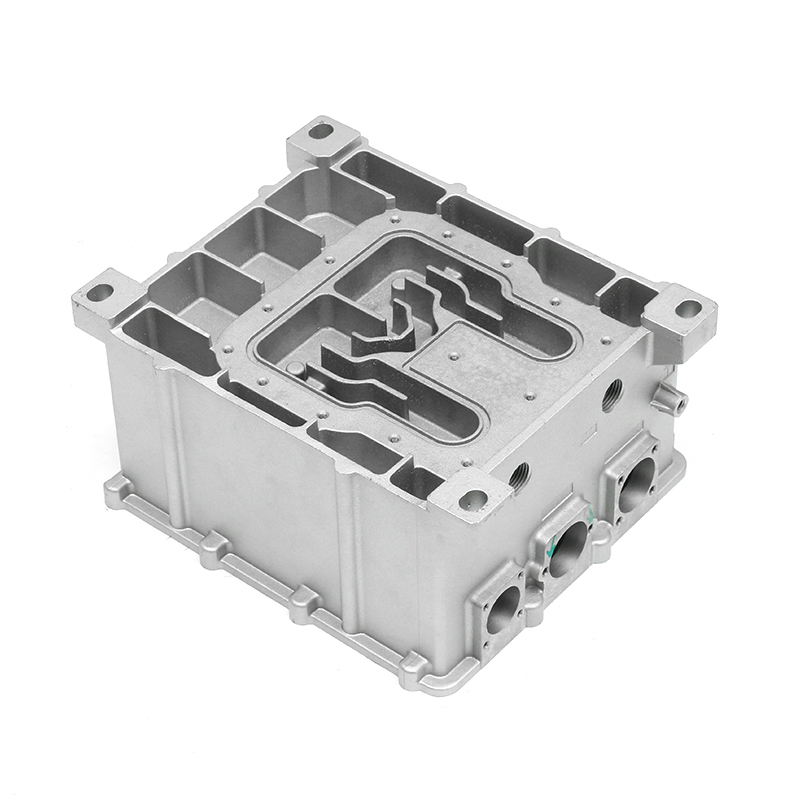
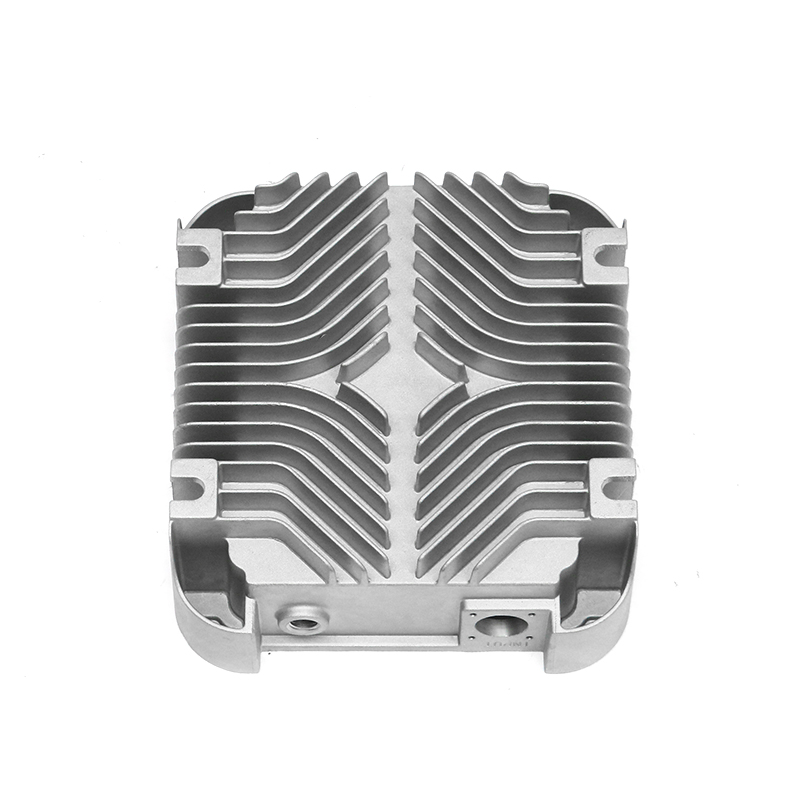
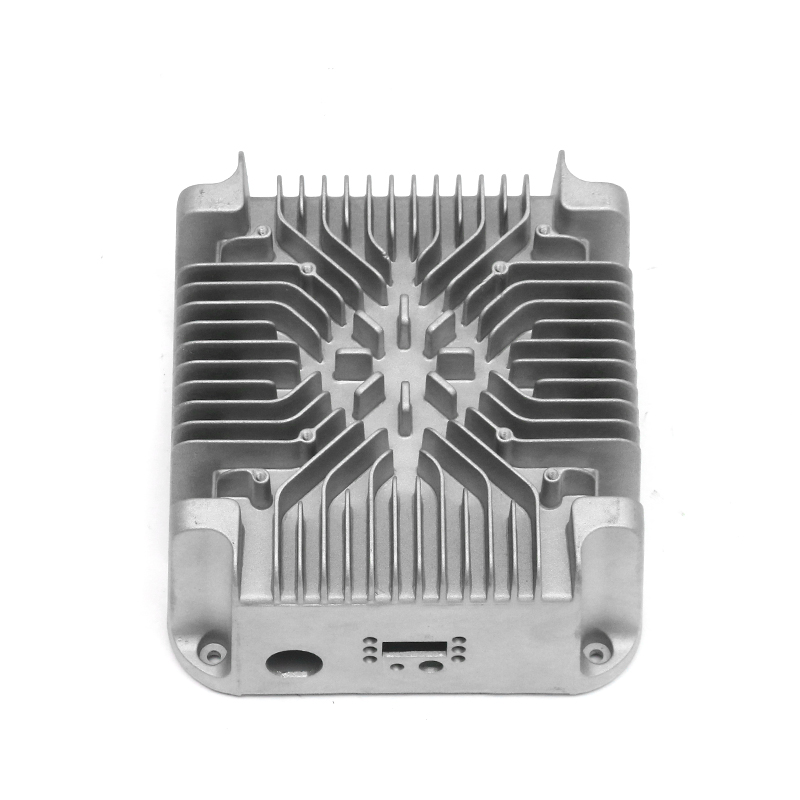
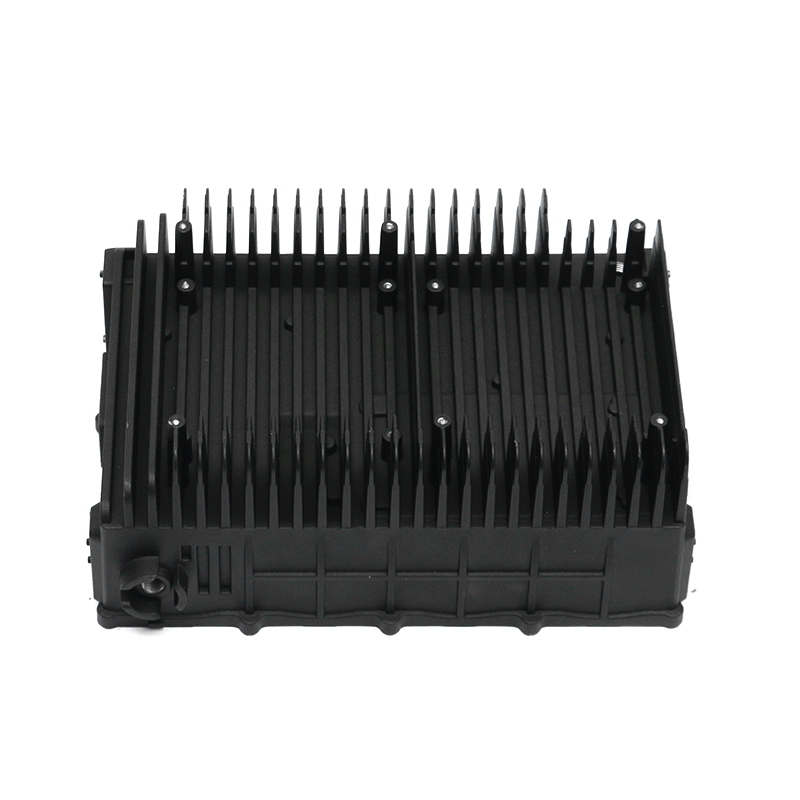
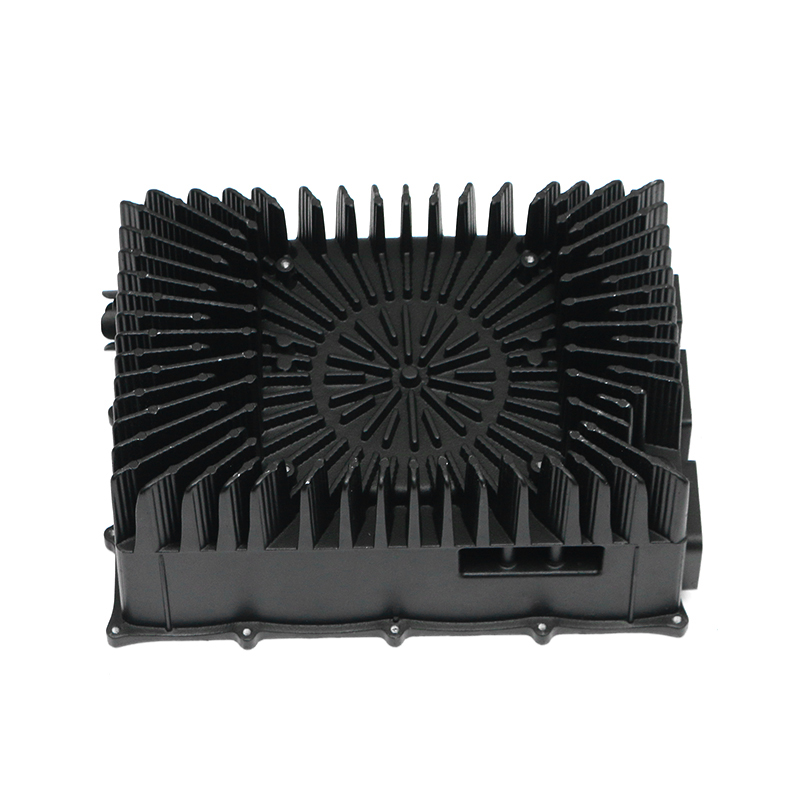
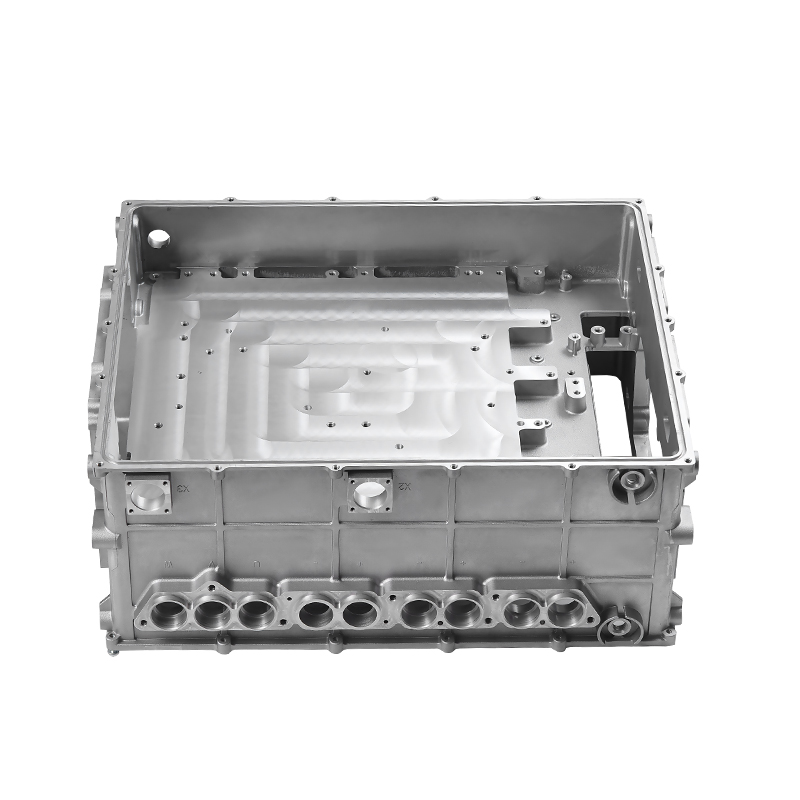
Introduction to New Energy Motor Housing Die Casting
Die casting is a widely used manufacturing process in which molten metal is injected under high pressure into a mold to form a specific shape. This method is highly valued for its ability to produce parts with complex geometries and high dimensional accuracy. In recent years, the demand for energy-efficient and sustainable technologies has led to the growth of the new energy sector, including electric vehicles (EVs), solar power systems, and other green energy solutions. The motor housing for these systems, particularly in electric motors, plays a crucial role in protecting the internal components while providing structural support. As a result, the production of motor housing through die casting has gained significant attention, with particular focus on its potential for waterproof and dustproof properties.
Understanding the Need for Waterproof and Dustproof Motor Housings
In the context of new energy applications, such as electric motors in electric vehicles or renewable energy generators, the motor housing must protect sensitive internal components like the rotor, stator, and electrical windings from environmental contaminants. The primary function of the housing is to shield these internal components from external factors such as water, dust, dirt, and other harmful materials that could compromise the motor's efficiency and lifespan.
Water and dust are two of the most common environmental threats that electric motors face. Water can cause electrical short circuits, rust, or corrosion in metal parts, while dust can clog vents, impair cooling, and damage the internal wiring or mechanical components. Therefore, ensuring that the motor housing has adequate waterproof and dustproof properties is crucial for maintaining the reliability and performance of new energy systems, particularly in demanding environments like automotive, industrial, and outdoor applications.
The Role of Die Casting in Creating Waterproof and Dustproof Properties
Die casting is particularly well-suited for producing motor housings with waterproof and dustproof properties due to its ability to produce complex shapes with tight tolerances and smooth surfaces. The high-pressure injection of molten metal ensures that the parts are dense and free of voids, which is essential for creating a solid, impermeable barrier that prevents water and dust from entering the motor housing.
One of the primary advantages of die casting is its ability to produce castings with thin walls and intricate designs while maintaining structural integrity. This ability to create intricate geometries, including ribs, bosses, and threaded holes, makes it possible to design motor housings with enhanced sealing features. For example, the housing can be designed with overlapping sections or grooves that help secure gaskets or O-rings, further preventing water or dust ingress.
Additionally, die-cast parts can be treated with various surface coatings and finishes that improve their resistance to moisture and contaminants. The choice of alloy, mold design, and post-processing treatments can all contribute to enhancing the housing's ability to withstand environmental challenges.
Materials Used in New Energy Motor Housing Die Casting
The choice of material plays a significant role in determining the waterproof and dustproof capabilities of die-cast motor housings. While various metals can be used for die casting, aluminum and zinc alloys are the most common materials for manufacturing motor housings in the new energy sector.
Aluminum is widely used for its lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and thermally conductive properties. It is particularly suitable for applications like electric vehicle motors, where weight reduction is important for improving efficiency and performance. Aluminum alloys used in die casting often contain small amounts of other metals, such as silicon and copper, to enhance their strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion. The corrosion resistance of aluminum is particularly valuable in protecting the motor housing from the damaging effects of water and moisture, thereby contributing to the housing's waterproof properties.
Zinc alloys, on the other hand, are known for their high strength, good castability, and resistance to oxidation. While zinc die-cast parts tend to be heavier than their aluminum counterparts, they offer advantages in applications where strength and durability are paramount. Zinc alloys can also be treated with various coatings, such as powder coatings or electroplating, to further enhance their resistance to water and dust ingress.
In both cases, the die-casting process allows for precise control over the material's composition and the mold design, which ensures that the motor housing has the necessary properties to protect internal components from environmental threats.
Sealing Mechanisms for Waterproof and Dustproof Performance
While the material and manufacturing process contribute to the inherent waterproof and dustproof properties of the motor housing, additional sealing mechanisms are often incorporated to enhance performance. Seals and gaskets are critical components that prevent the ingress of water, dust, and other contaminants into the motor housing. These seals are usually placed at key joints and interfaces, such as where the housing sections meet or around areas where electrical wires or connectors pass through.
In die-cast motor housings, the design of these joints can be optimized to improve sealing. For example, the housing can be designed with grooves or channels that allow for the placement of rubber O-rings, gaskets, or silicone seals. These seals create a tight, secure barrier that prevents water and dust from entering, even under high-pressure conditions.
In addition to mechanical seals, the use of adhesive bonding and special coatings can further improve the waterproof and dustproof capabilities of the motor housing. For example, some die-cast motor housings are treated with a thin layer of silicone or polyurethane coatings that offer additional protection against moisture and dust. These coatings are applied during the post-processing stage and can significantly enhance the overall durability of the housing.
Testing Waterproof and Dustproof Properties
To ensure that die-cast motor housings meet the necessary standards for waterproof and dustproof performance, various testing methods are employed. One of the most common testing standards used to evaluate the sealing effectiveness of motor housings is the International Protection (IP) rating system. The IP rating system classifies the level of protection provided by an enclosure against the ingress of solids (dust) and liquids (water).
The IP rating consists of two digits. The first digit indicates the level of protection against solid objects, such as dust or dirt, while the second digit indicates the level of protection against water. For example, an IP65 rating means the motor housing is fully protected against dust and can withstand water jets from any direction. An IP67 rating provides even higher protection, indicating that the housing is dust-tight and can be submerged in water for a certain period without compromising its integrity.
Through rigorous testing, manufacturers can ensure that their die-cast motor housings meet the required standards for waterproof and dustproof performance. These tests help guarantee that the housing will protect the internal components of the motor, ensuring reliable performance even in harsh environments.
Benefits of Waterproof and Dustproof Die-Cast Motor Housings
Motor housings that are both waterproof and dustproof offer several benefits, especially in the context of new energy applications. First and foremost, these properties help increase the longevity and reliability of the motor by preventing environmental factors from causing damage. In electric vehicles, for example, the motor housing must protect sensitive electrical components from water and dust, which could otherwise lead to electrical failures or reduced efficiency.
Additionally, waterproof and dustproof motor housings contribute to the overall safety of the system. Water ingress can cause short circuits, while dust can interfere with the motor's cooling system, leading to overheating or even mechanical failure. By preventing these issues, die-cast motor housings can enhance the safety of the equipment, reducing the risk of breakdowns or malfunctions.
From an environmental standpoint, waterproof and dustproof motor housings also help reduce maintenance needs and operational downtime. When the motor is protected from external elements, the need for frequent repairs or replacements is minimized, leading to cost savings for businesses and end-users. Furthermore, these properties help maintain the efficiency of the motor by ensuring that cooling systems are not clogged by dust and that the motor's components remain protected from corrosion or wear caused by water exposure.