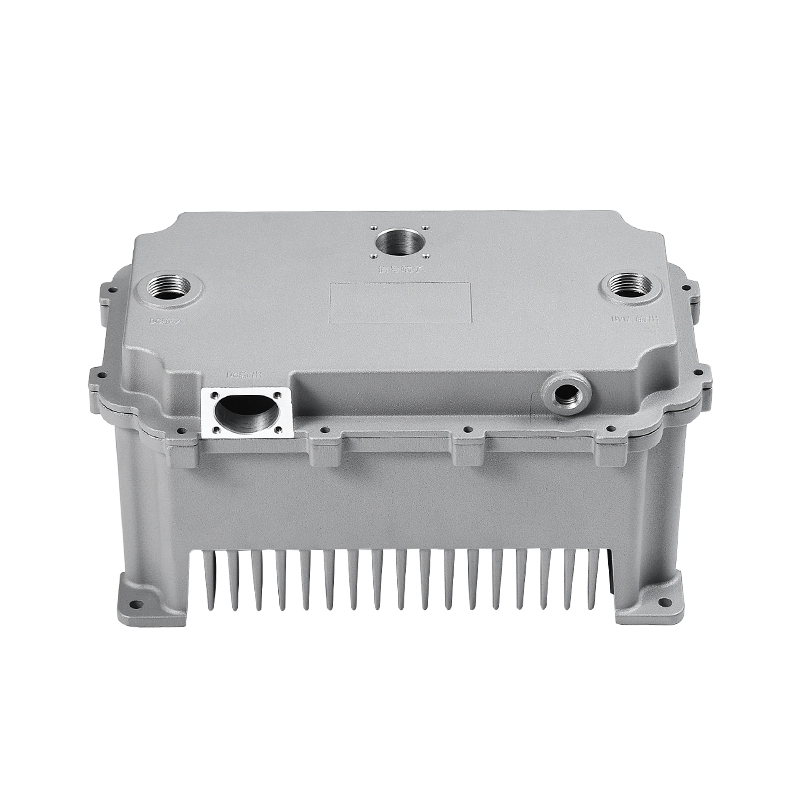
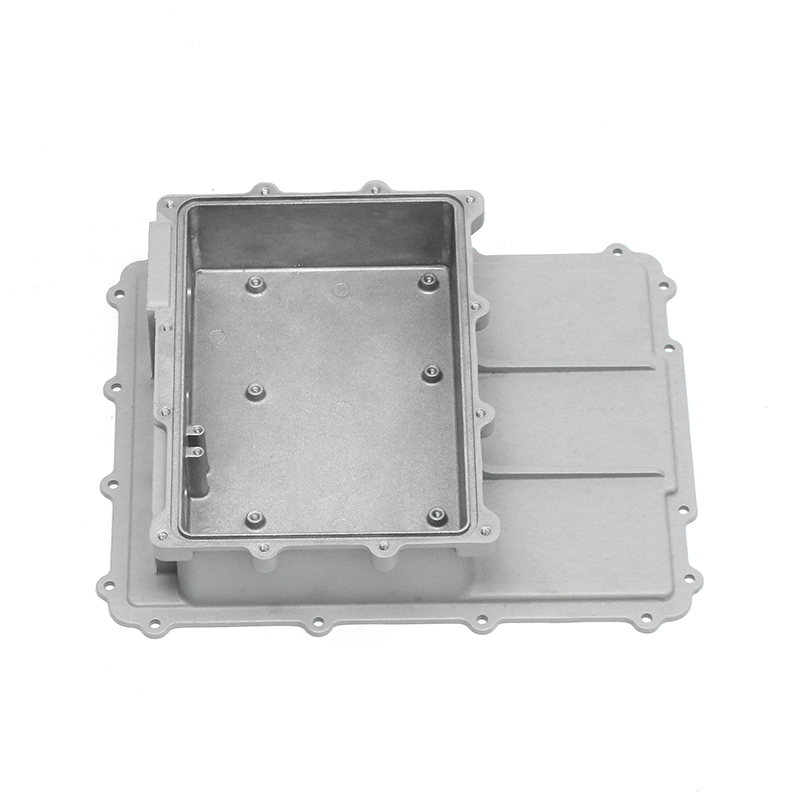
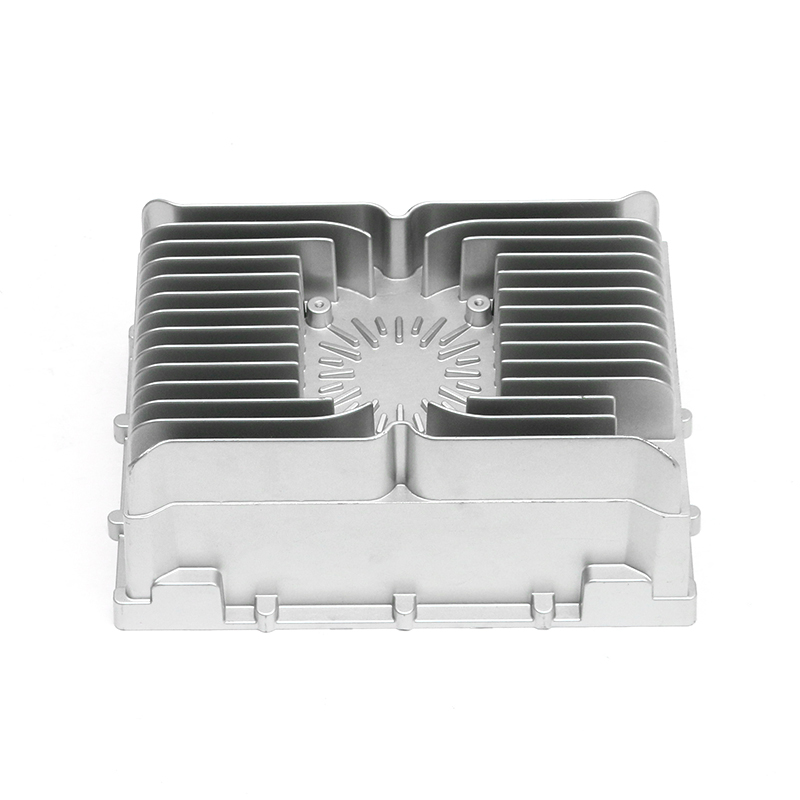
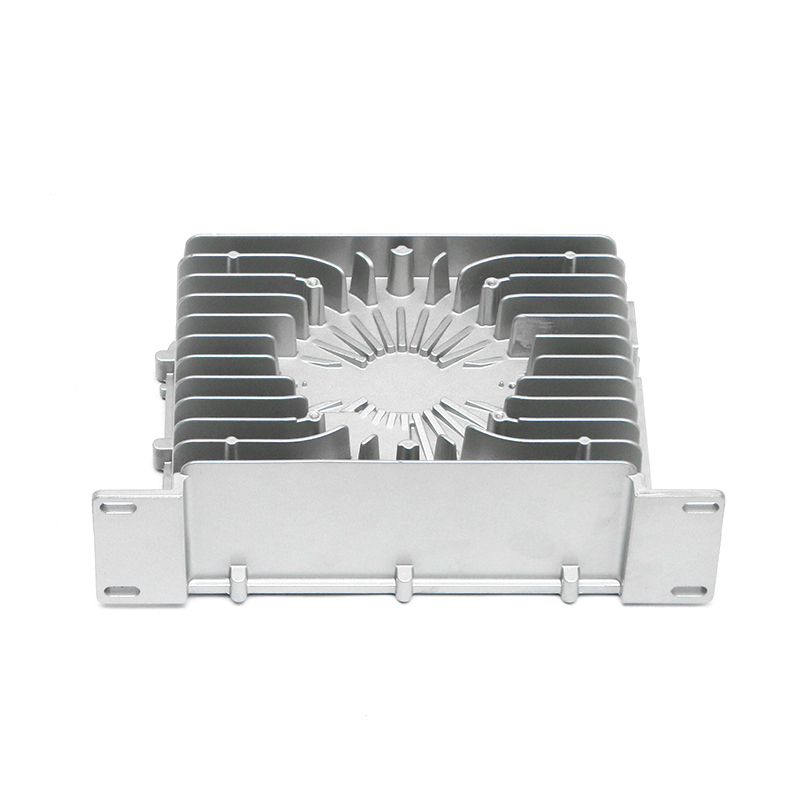
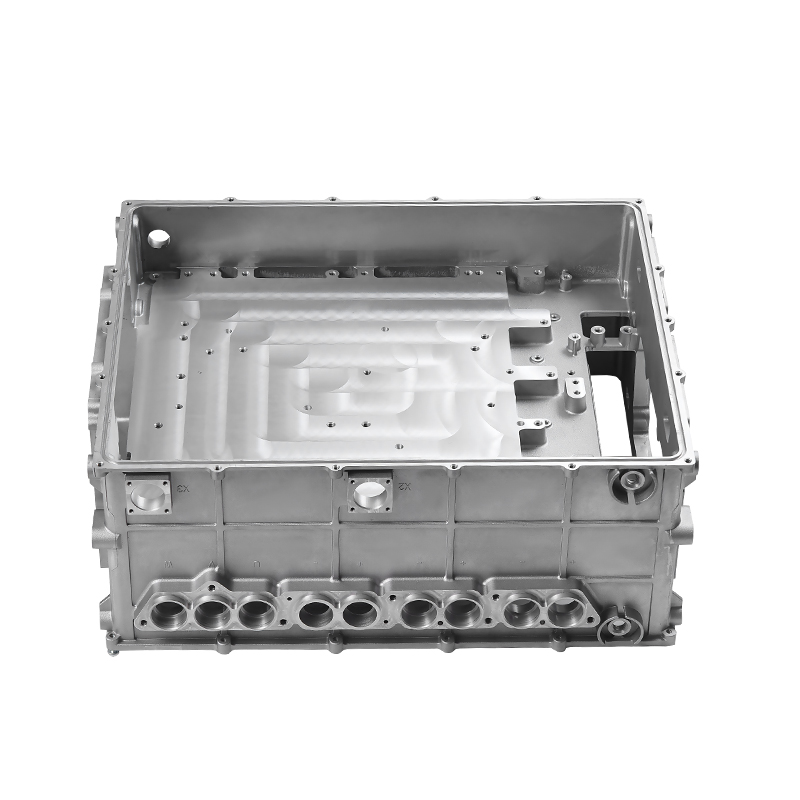
Overview of Die Casting in New Energy Vehicle Motor Housings
The die casting process is widely employed in the manufacturing of motor housings for new energy vehicles due to its ability to produce precise, complex, and high-strength components. Motor housings must fulfill multiple performance criteria, including structural integrity, heat dissipation, and vibration damping, to ensure reliability and longevity of the electric motor. Optimizing both thermal management and vibration control during the die casting process has become a critical focus for manufacturers aiming to improve vehicle performance and reduce maintenance requirements.
Importance of Heat Dissipation in Motor Housings
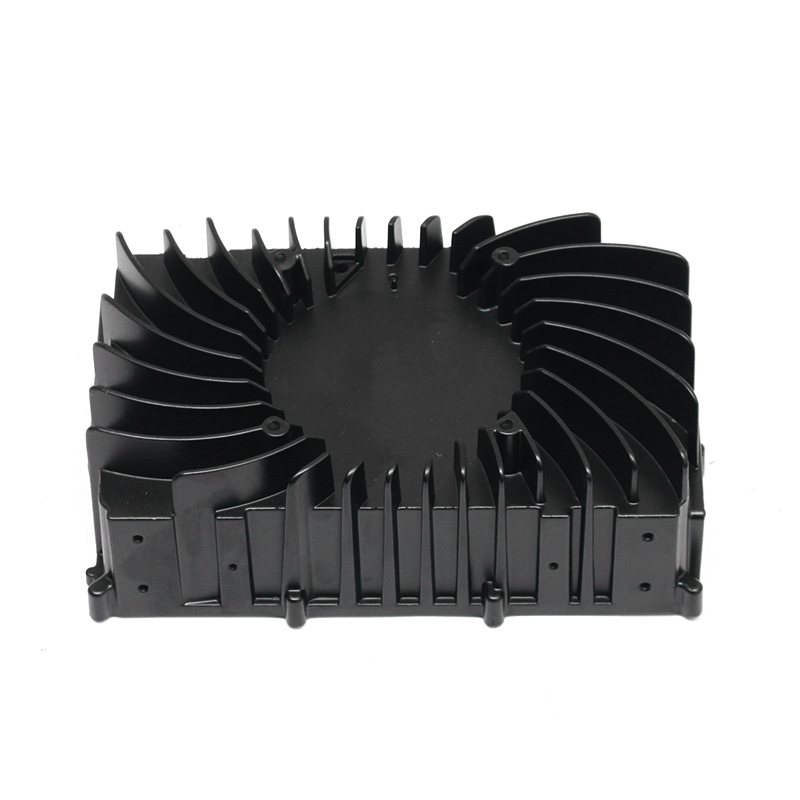
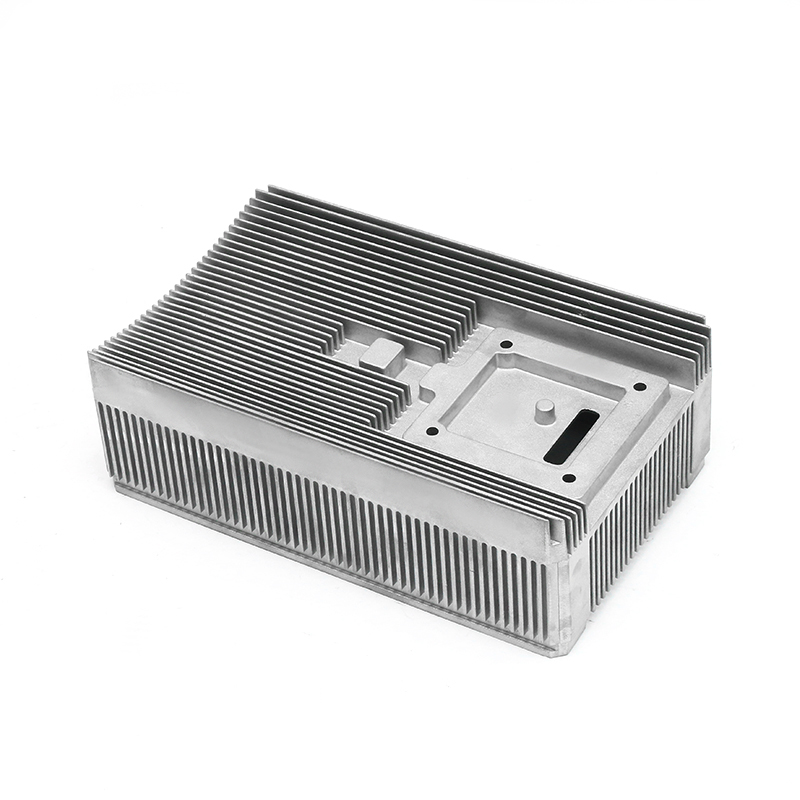
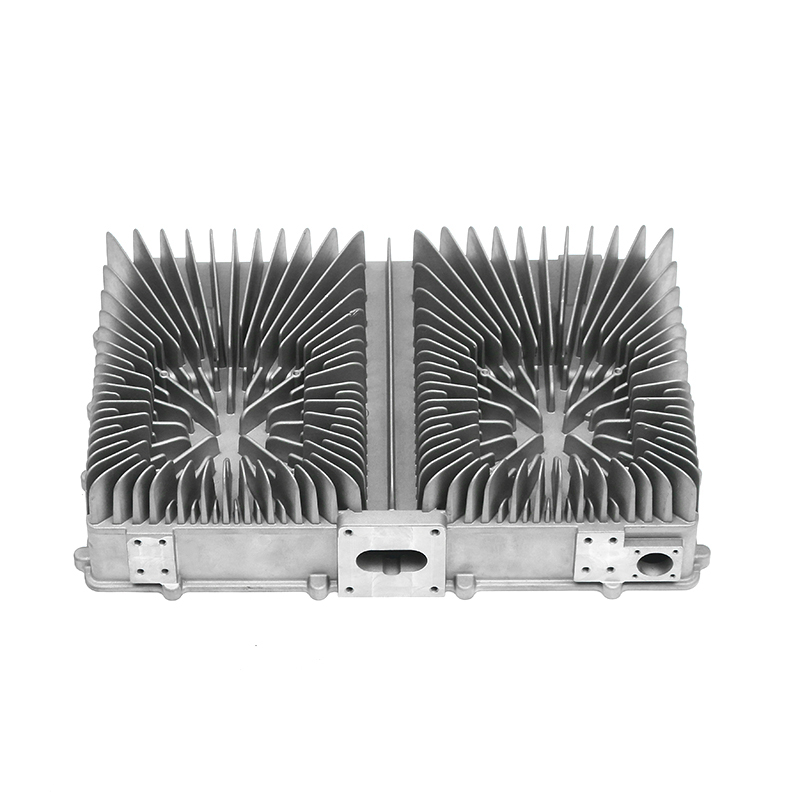
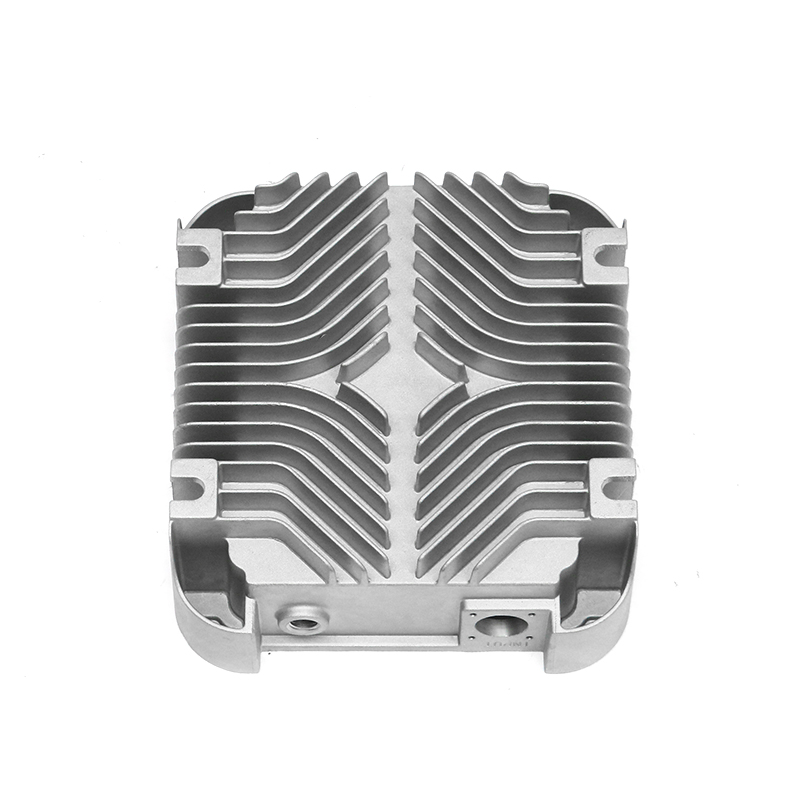
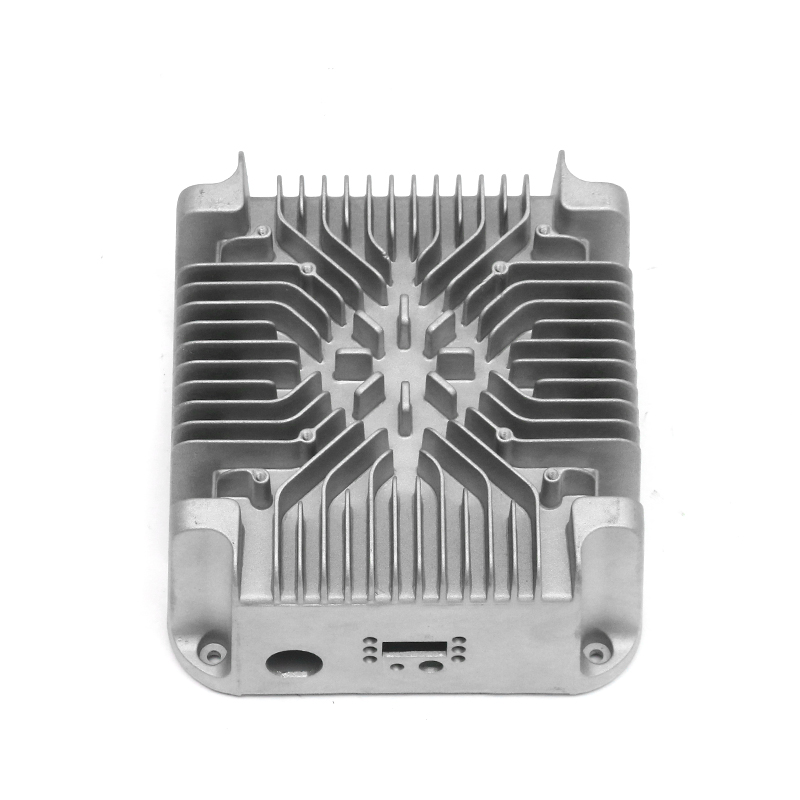
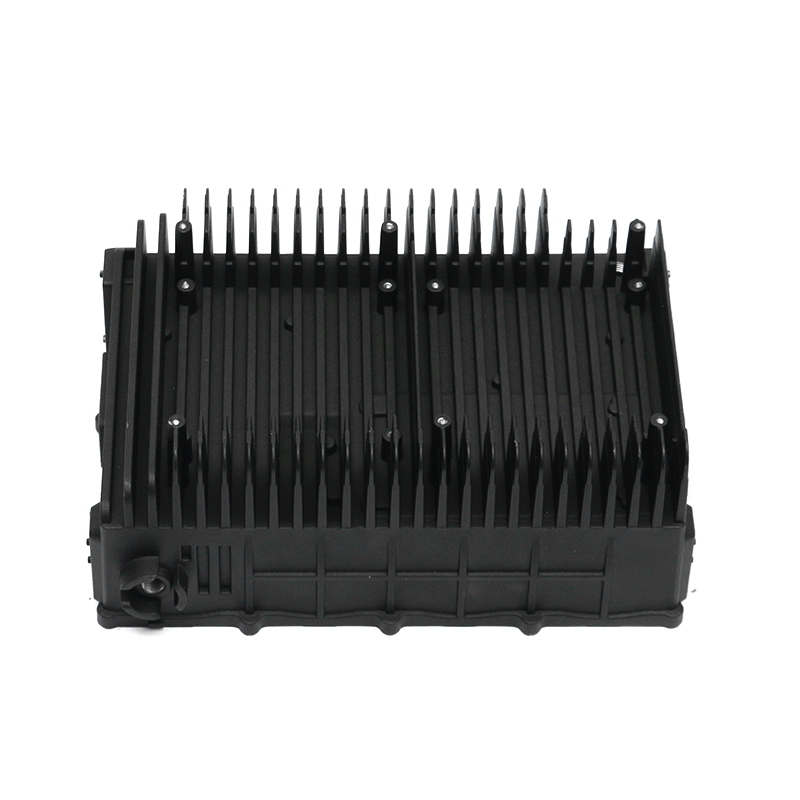
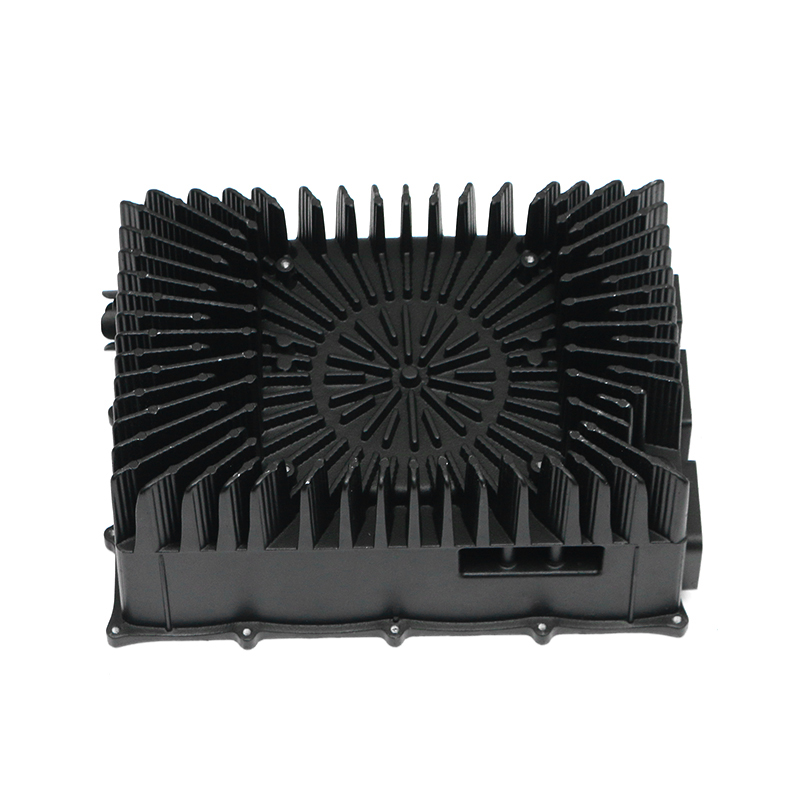
Effective heat dissipation in motor housings is essential to maintain motor efficiency and prevent overheating. Electric motors generate significant heat during operation, and excessive temperatures can accelerate wear, degrade insulation materials, and reduce overall performance. Die casting allows for the integration of cooling fins, ribs, and other geometrical features directly into the housing, enhancing the surface area available for heat transfer. Material selection, alloy composition, and precise control of wall thickness further influence the thermal conductivity and heat dissipation capacity of the motor housing.
Die Casting Techniques to Enhance Thermal Management
During the die casting process, controlled cooling rates and mold temperature management contribute to the thermal properties of the finished motor housing. Rapid solidification can produce fine-grained structures with higher thermal conductivity, while uniform wall thickness minimizes hotspots that could compromise performance. Additionally, surface treatments or coatings applied post-casting can improve thermal emissivity, further enhancing the housing’s ability to dissipate heat generated during motor operation.
Vibration Damping Requirements for Motor Housings
Electric motors in new energy vehicles produce vibrations due to rotor rotation, electromagnetic forces, and torque fluctuations. These vibrations can lead to noise, component fatigue, and accelerated wear if not properly managed. Motor housings must therefore exhibit sufficient damping characteristics to absorb and mitigate vibration energy. The die casting process allows engineers to optimize internal structures, wall geometry, and material properties to improve the housing’s capacity to reduce vibrational amplitude and maintain structural integrity over time.
Alloy Selection and Its Role in Vibration Control
The choice of die casting alloy affects both thermal and vibration performance. Aluminum and its alloys are commonly used for motor housings because they provide a balance of lightweight characteristics, thermal conductivity, and moderate damping capability. Additives and secondary alloying elements can enhance stiffness and reduce susceptibility to vibration-induced fatigue. The combination of alloy selection and die casting parameters ensures that the motor housing meets both heat dissipation and vibration damping requirements without compromising manufacturability.
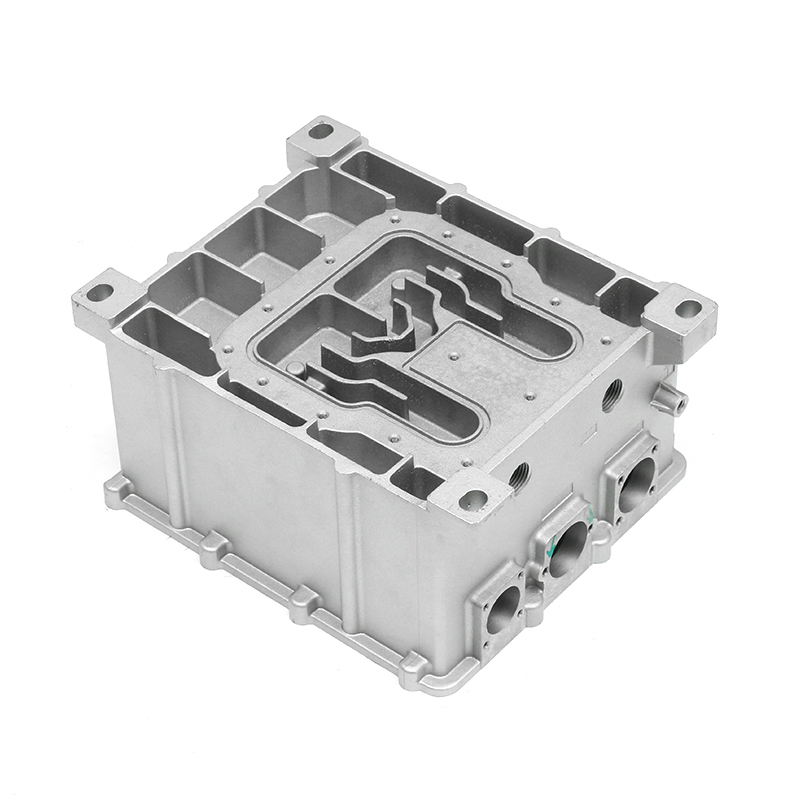
Optimizing Wall Thickness and Structural Design
Wall thickness and structural layout are critical parameters that influence heat and vibration performance. Uniform wall thickness improves thermal transfer by reducing insulation effects and preventing hotspots. Simultaneously, ribs, gussets, and strategically placed reinforcements can enhance stiffness and reduce vibration transmission. During the die casting design phase, computational modeling often evaluates the trade-offs between thermal performance and mechanical damping, guiding adjustments to geometry before manufacturing.
Use of Fin Designs for Thermal Management
Cooling fins integrated into the die-cast housing increase surface area and facilitate heat exchange with the surrounding air. Die casting allows these features to be formed directly during production, avoiding additional assembly steps. The orientation, spacing, and thickness of fins are carefully designed to balance thermal performance with weight and structural rigidity. Proper fin design helps maintain optimal motor temperatures under continuous operation and transient load conditions.
Integration of Vibration-Reducing Features
Die casting provides the flexibility to integrate internal vibration-reducing features such as damping ribs, hollow cavities, and strategically thickened sections. These features absorb vibrational energy and reduce resonance, improving noise and vibration comfort. Engineers often use finite element analysis (FEA) to simulate vibration modes and identify areas where structural adjustments are most effective in damping oscillations without adding excessive weight.
Surface Treatments and Post-Casting Enhancements
Post-casting processes can enhance both heat dissipation and vibration performance. Anodizing or thermal coatings increase emissivity and improve thermal radiation, aiding heat removal. Additionally, vibration damping pads or polymer-based coatings can be applied to specific regions to mitigate residual vibrations. These post-casting enhancements complement the structural design achieved during die casting and extend the functional lifespan of the motor housing.
Comparing Die Casting Factors Affecting Heat Dissipation and Vibration Damping
| Factor | Impact on Heat Dissipation | Impact on Vibration Damping |
|---|---|---|
| Alloy composition | Higher thermal conductivity improves cooling efficiency | Material stiffness and density influence damping capacity |
| Wall thickness | Uniform thickness reduces hotspots | Thicker walls increase stiffness, affecting vibration response |
| Internal ribs and gussets | Minimal impact on heat transfer if designed carefully | Enhances structural rigidity and vibration absorption |
| Cooling fins | Increases surface area for improved thermal dissipation | May alter natural frequencies, affecting vibration modes |
| Post-casting treatments | Coatings enhance emissivity and surface heat transfer | Damping layers or pads reduce residual vibration amplitudes |
Simulation and Testing for Optimization
Before production, simulation tools such as computational fluid dynamics (CFD) and finite element analysis (FEA) are applied to predict thermal and vibrational behavior. CFD evaluates airflow and heat transfer efficiency, while FEA examines stress distribution and vibration modes. Iterative adjustments to die casting geometry, wall thickness, and rib placement allow engineers to optimize the balance between heat dissipation and vibration damping. Prototype testing confirms simulation predictions and identifies any adjustments needed for production-scale performance.
Weight Considerations and Performance Trade-Offs
New energy vehicle motor housings must balance thermal and vibrational performance with weight limitations, as reducing mass contributes to overall vehicle efficiency. Die casting allows complex geometries that provide necessary cooling and damping without excessive material usage. Lightweight designs maintain structural integrity while optimizing heat removal and vibration control. Careful evaluation of these trade-offs ensures that the final housing meets performance, safety, and efficiency requirements.
Quality Control and Process Stability
Maintaining consistent die casting process parameters is essential to ensure repeatable heat dissipation and vibration damping performance. Factors such as mold temperature, injection speed, and solidification rate influence grain structure, porosity, and surface finish. Quality control measures, including inspection of wall thickness, dimensional accuracy, and material properties, help maintain consistency across production batches. Stable die casting processes reduce variability and enhance both thermal and vibrational performance in the final motor housings.
Environmental and Operational Considerations
Motor housings in new energy vehicles are exposed to varying environmental conditions, including temperature fluctuations, humidity, and mechanical loads. Die casting optimization ensures that housings maintain thermal management and vibration damping properties under these conditions. Properly designed housings help preserve motor performance, reduce noise, and contribute to long-term reliability, even under harsh operating environments.
Integration with Motor Assembly
The die-cast motor housing must integrate seamlessly with the rotor, stator, and other motor components. Interface surfaces, mounting points, and structural features are carefully designed to support heat transfer and vibration reduction at critical contact points. Effective integration ensures that heat generated in the motor core is efficiently conducted to the housing and that vibrations are dampened before reaching other vehicle components. This holistic approach enhances overall motor performance.
Continuous Improvement in Die Casting Processes
Manufacturers continuously refine die casting parameters and material compositions to enhance both heat dissipation and vibration damping. Advancements in mold design, thermal simulation, and alloy technology allow incremental improvements in performance. Ongoing research and development focus on maximizing cooling efficiency while maintaining sufficient vibration absorption, ensuring that new energy vehicle motor housings meet evolving industry standards and operational demands.