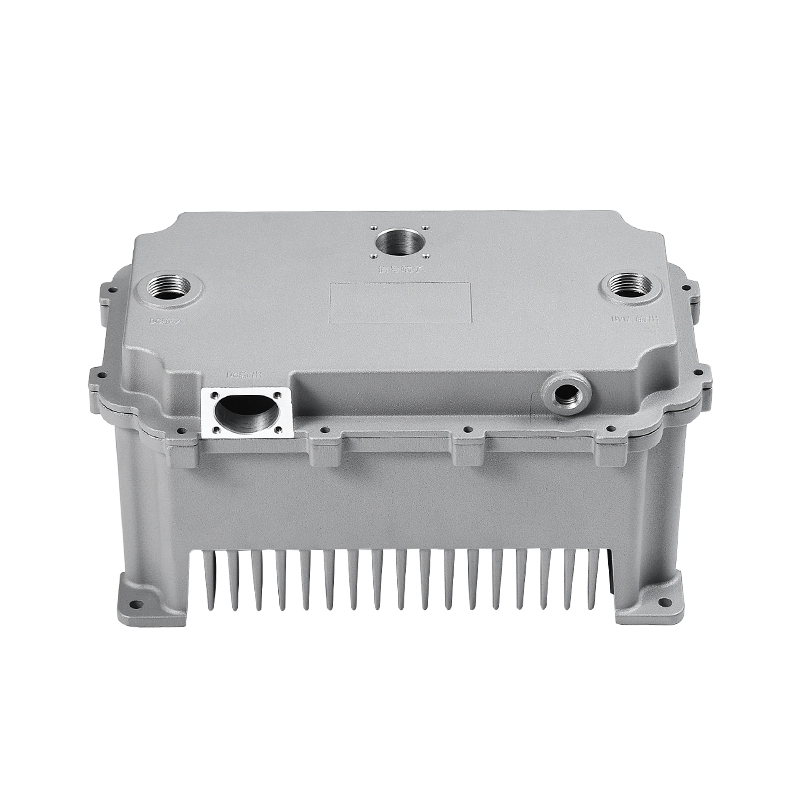
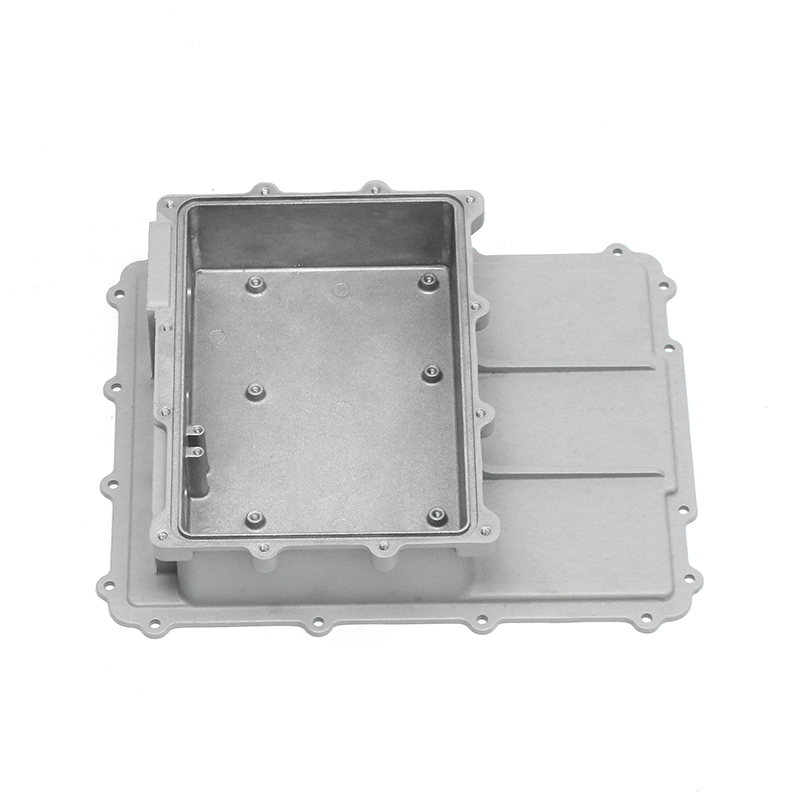
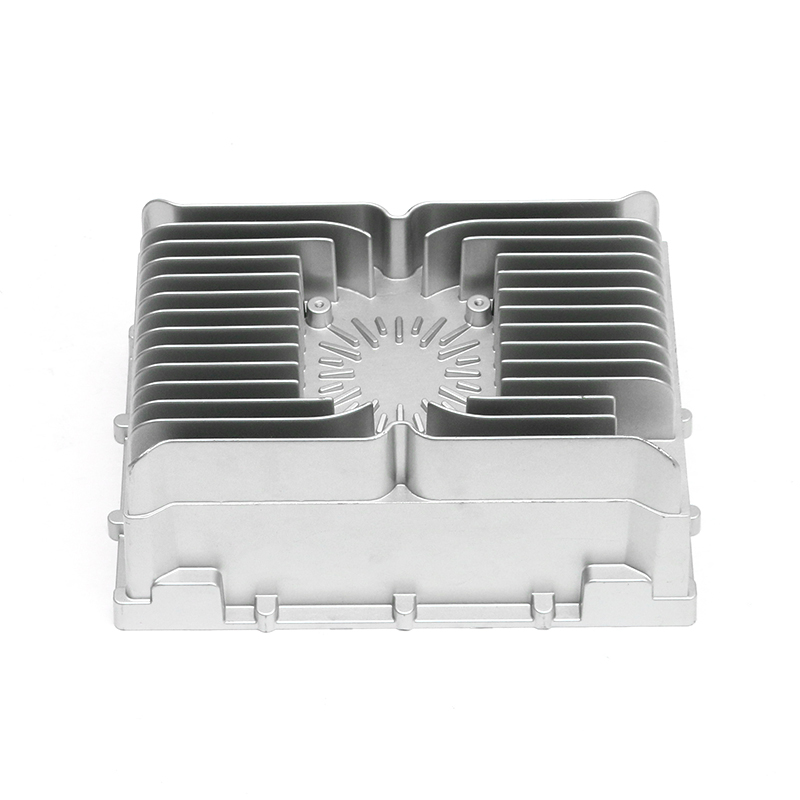
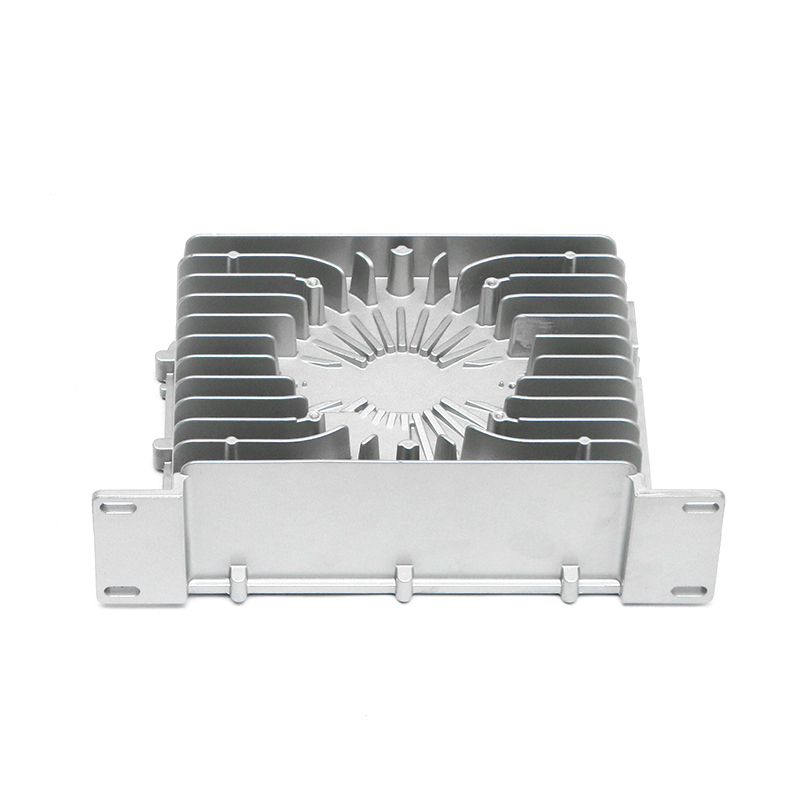
Overview of new energy electronically controlled air-cooled series die castings
New energy electronically controlled air-cooled series die castings are components widely used in electric vehicle systems, renewable energy applications, and high-performance electronic devices. These castings often serve as housings, heat sinks, or structural supports for sensitive electronics, combining mechanical strength with thermal management. Ensuring dimensional and performance consistency during mass production requires a comprehensive approach that addresses material properties, die design, process control, and quality monitoring. Each factor contributes to maintaining uniformity across large production batches while meeting performance requirements.
Material selection and consistency
Material properties are fundamental to the stability of die castings. Aluminum alloys are commonly used for air-cooled series die castings due to their lightweight, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance. Consistency in chemical composition, particle distribution, and temperature history of the alloy ensures uniform flow, solidification, and mechanical properties. Suppliers of raw materials often provide certification of chemical composition and traceability, which forms the first layer of control over dimensional and performance uniformity.
Die design considerations for dimensional accuracy
Dimensional consistency starts with careful die design. Dies must account for material shrinkage, thermal expansion, and potential warping during cooling. Advanced software simulations, such as finite element analysis (FEA) and casting flow modeling, predict areas of potential deviation and allow optimization of gating, venting, and cooling channels. By anticipating the effects of thermal and mechanical stress, die designers can create molds that produce uniform dimensions even under high-volume production conditions.
Process parameter control during die casting
Die casting involves injecting molten metal into a mold under high pressure. Maintaining consistent process parameters—such as injection speed, pressure, temperature, and shot volume—is critical for dimensional and performance stability. Variations in any parameter can lead to porosity, surface defects, or deviations in wall thickness. Modern die casting machines often include closed-loop control systems that monitor and adjust these parameters in real time, ensuring consistent results across thousands of cycles.
Temperature management in air-cooled die castings
Temperature consistency plays a significant role in both dimensional stability and mechanical performance. Air-cooled die castings require precise management of mold temperature, metal pouring temperature, and cooling rate. Uneven cooling can result in residual stress, warping, or inconsistent microstructure, affecting both strength and thermal performance. Integrated cooling channels, controlled airflow, and thermal sensors help maintain consistent temperature profiles throughout production.
Shot-to-shot repeatability and machine calibration
Ensuring dimensional and performance consistency requires that every injection of molten metal behaves similarly. Regular machine calibration, including verification of plunger alignment, shot weight, and pressure curves, is necessary. Equipment maintenance schedules and real-time monitoring reduce variations caused by wear or mechanical drift. Repeatable machine behavior directly influences casting uniformity, particularly for complex geometries.
Quality inspection and measurement systems
Dimensional accuracy and performance consistency are verified through a combination of manual and automated inspection methods. Coordinate measuring machines (CMM), laser scanners, and optical inspection systems capture precise dimensions for comparison against design specifications. Non-destructive testing (NDT) methods, such as X-ray or ultrasonic inspection, identify internal defects that could compromise performance. Statistical process control (SPC) tracks trends over time, allowing early detection of deviations and corrective action before defective parts are produced in large quantities.
Controlling shrinkage and warpage
Shrinkage and warpage are common issues in die casting due to metal solidification and cooling. Optimizing die temperature, gating system design, and cooling rates helps minimize these effects. Simulation tools allow prediction of potential shrinkage locations and enable engineers to incorporate compensatory features in the die. Post-casting treatments, such as stress relieving or controlled aging, further stabilize dimensions and mechanical properties.
Surface finish and secondary machining considerations
Surface quality and secondary machining also impact performance consistency. Maintaining uniform surface finish reduces stress concentration and supports consistent thermal performance in air-cooled applications. Secondary operations, such as drilling, tapping, or milling, must be executed with precise jigs and fixtures to ensure that all castings meet the same geometric and functional criteria. Consistent surface and feature quality contribute to overall performance reliability.
Process standardization and operator training
Human factors are critical in mass production. Standardized operating procedures, detailed work instructions, and trained personnel reduce variability. Operators are responsible for monitoring machine parameters, verifying material conditions, and performing routine checks. Comprehensive training ensures that deviations are identified promptly and corrected before affecting dimensional or performance consistency.
Environmental controls in the production area
Ambient conditions in the manufacturing area, such as temperature, humidity, and dust levels, can influence die casting consistency. Controlled environments minimize oxidation, moisture absorption, and temperature fluctuations that could affect metal flow and solidification. Clean, temperature-stable facilities support repeatable results in both dimensions and functional performance of die cast components.
| Control Area | Impact on Consistency | Monitoring/Management Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Material Quality | Influences flow, solidification, mechanical properties | Supplier certification, chemical analysis, batch traceability |
| Die Design | Controls dimensional stability and shrinkage compensation | FEA simulation, flow analysis, prototype testing |
| Process Parameters | Ensures repeatable filling, pressure, and temperature | Closed-loop control, real-time monitoring, SPC |
| Temperature Management | Reduces warpage and residual stress | Mold sensors, cooling channel control, airflow management |
| Inspection and Quality Control | Verifies dimensions and internal integrity | CMM, laser scanning, X-ray, ultrasonic testing, SPC |
Role of automation and data analytics
Automation enhances dimensional and performance consistency by reducing human variability and allowing real-time monitoring. Sensors integrated with data analytics can detect minor deviations and adjust machine parameters accordingly. Feedback loops facilitate continuous improvement, ensuring that mass-produced die castings meet precise specifications consistently.
Post-casting treatments and their influence
Heat treatment, surface finishing, and stress relieving post-casting can improve performance stability. These treatments help reduce residual stresses, homogenize microstructure, and stabilize dimensions. Controlled post-processing ensures that all castings achieve similar mechanical and thermal properties before assembly or delivery.
Statistical process control and continuous improvement
Implementing statistical process control techniques helps monitor variations in key dimensions and functional characteristics. Control charts, process capability indices, and trend analysis support proactive adjustments. Continuous improvement programs, informed by production data, reduce variability over time and enhance both dimensional and performance consistency across large batches.
Supply chain and raw material traceability
Traceability of raw materials and components ensures that only verified and consistent inputs are used in production. Documented supply chain practices allow identification of deviations caused by material inconsistencies. When combined with in-process monitoring, traceability contributes to reliable performance of the die castings in their final applications.
Coordination between design, engineering, and production teams
Ensuring dimensional and performance consistency requires collaboration across multiple teams. Design engineers, process engineers, and production staff must communicate effectively to address potential challenges before and during mass production. Early identification of critical features, tolerance zones, and functional requirements supports consistent outcomes and reduces production risks.
Key factors in mass production stability
Consistency in mass-produced die castings relies on integrating material control, die design, process parameter management, temperature control, quality inspection, and operator training. Each element contributes to minimizing variation and ensuring that components meet both dimensional and functional specifications throughout production runs. Systematic monitoring, feedback, and continuous improvement provide the foundation for reliable large-scale manufacturing.