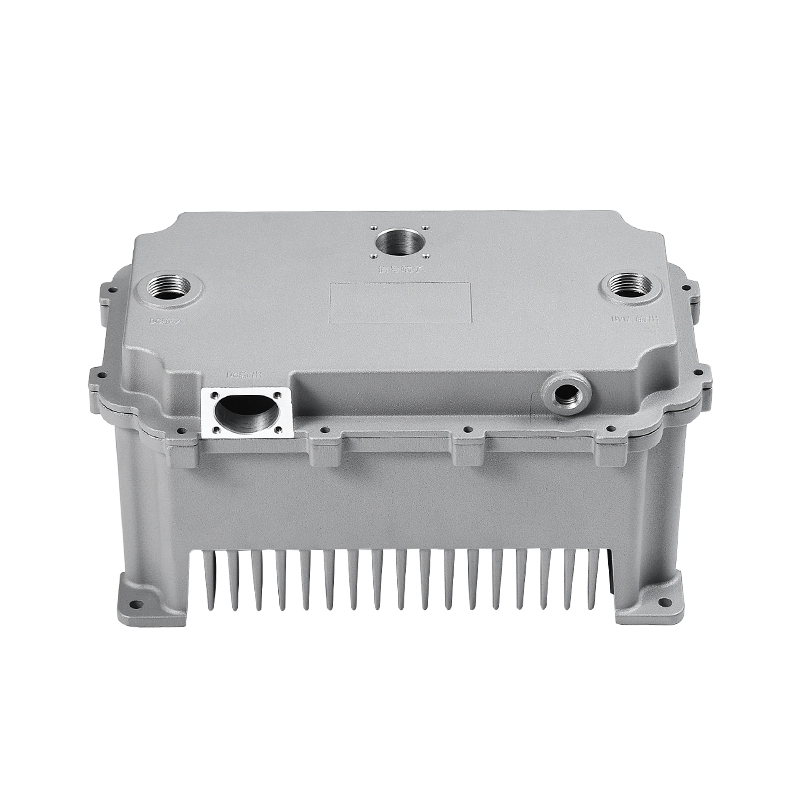
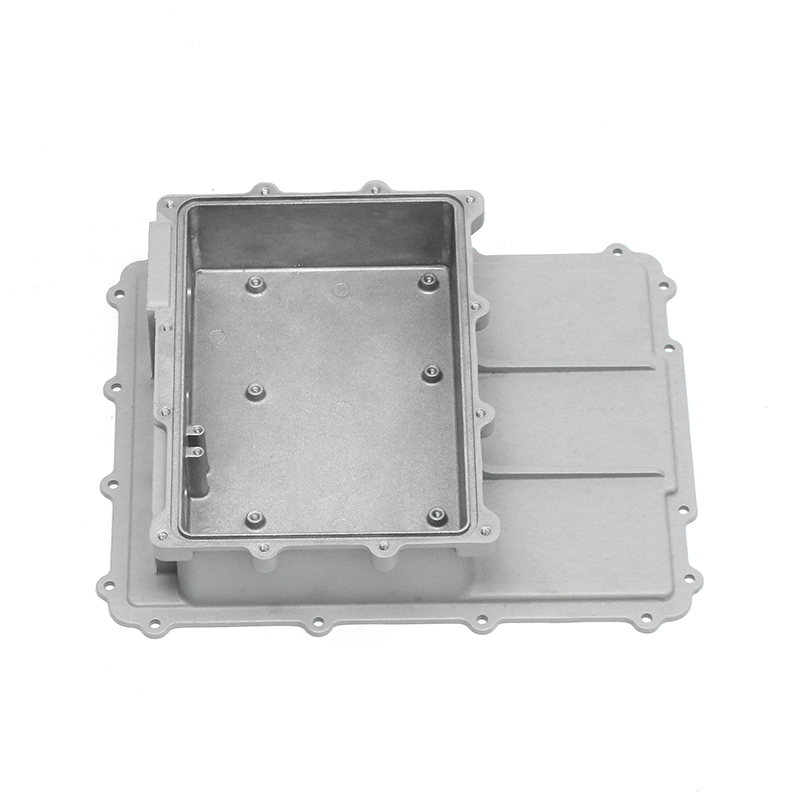
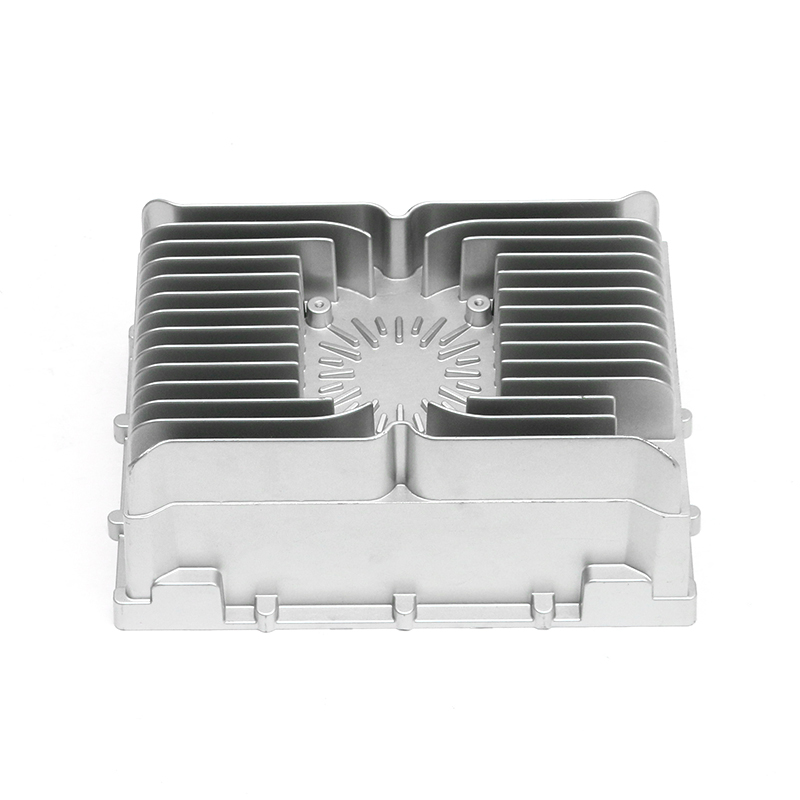
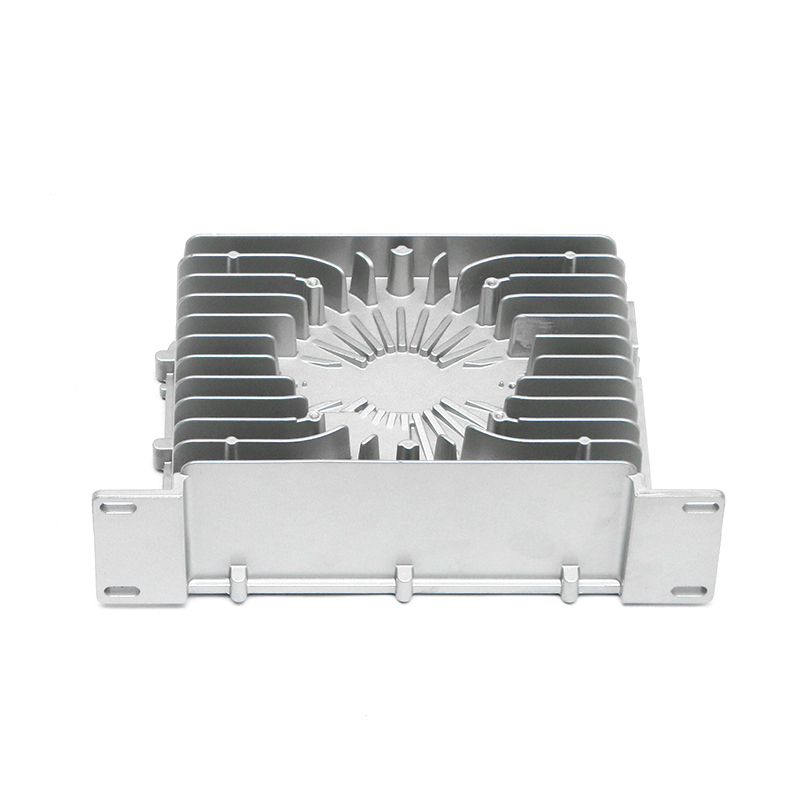
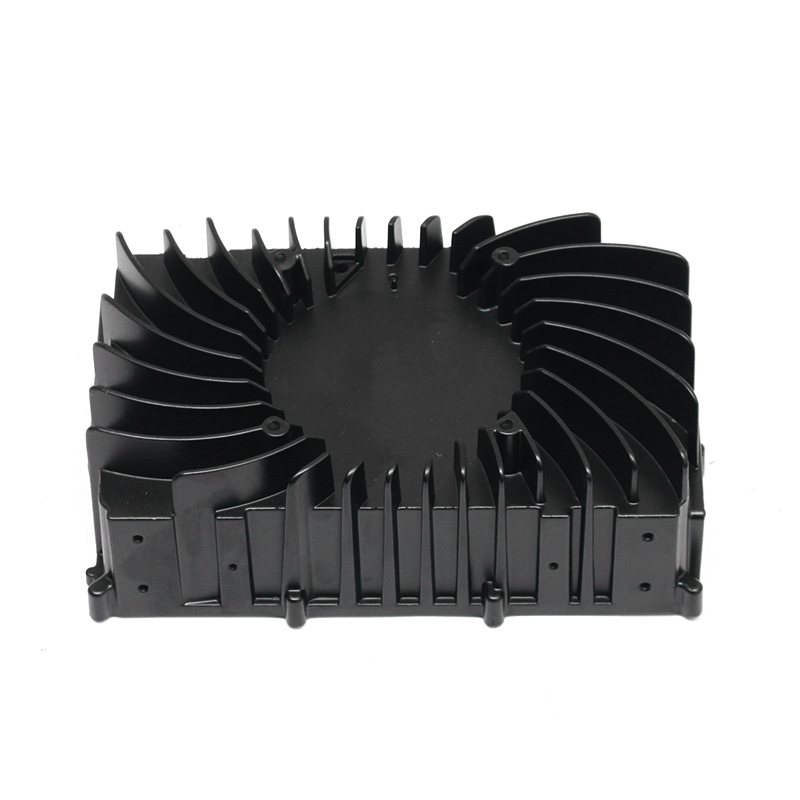
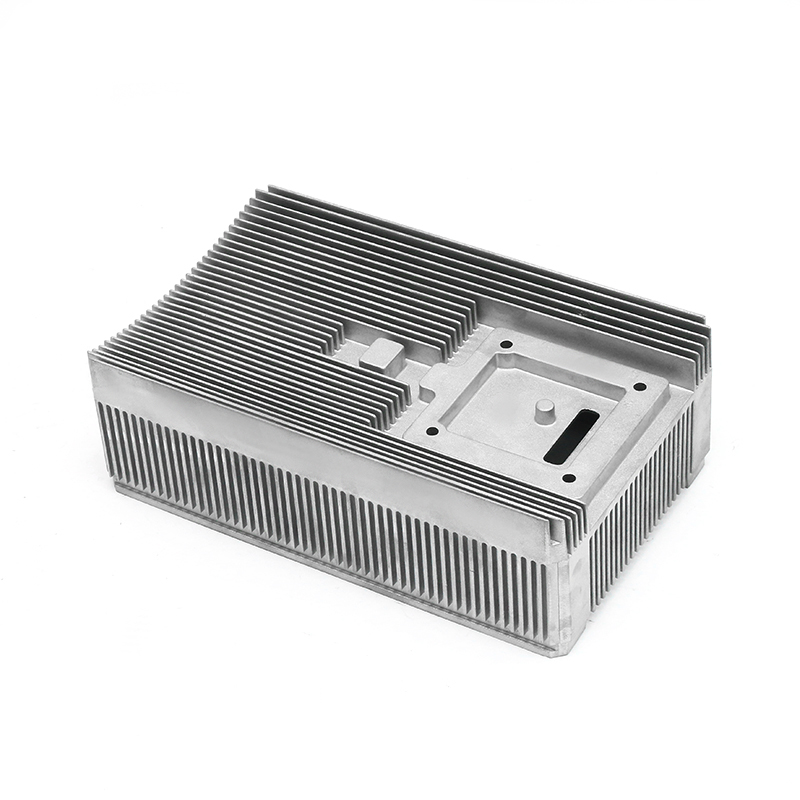
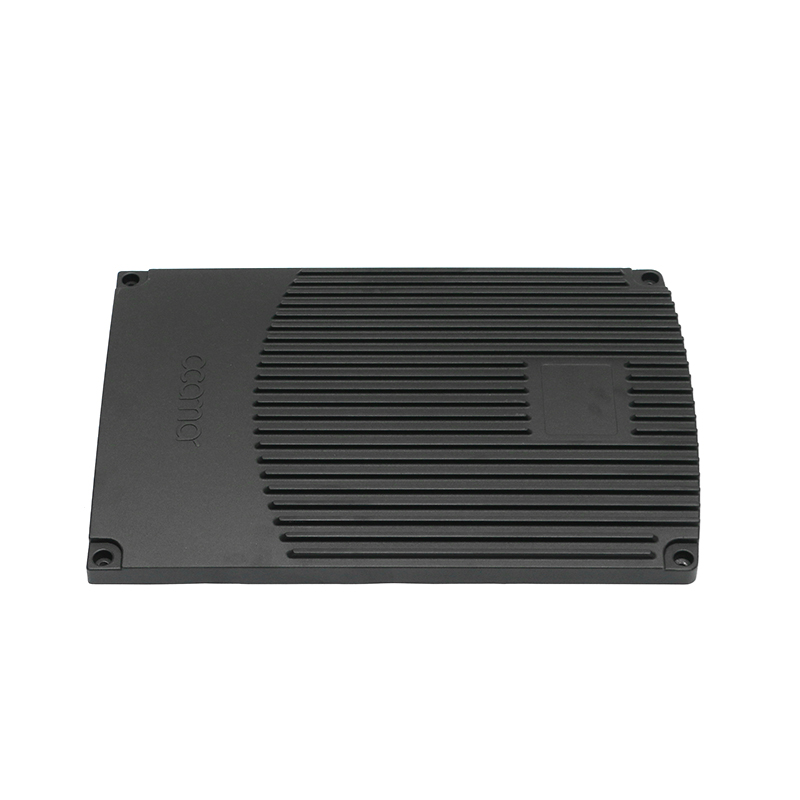
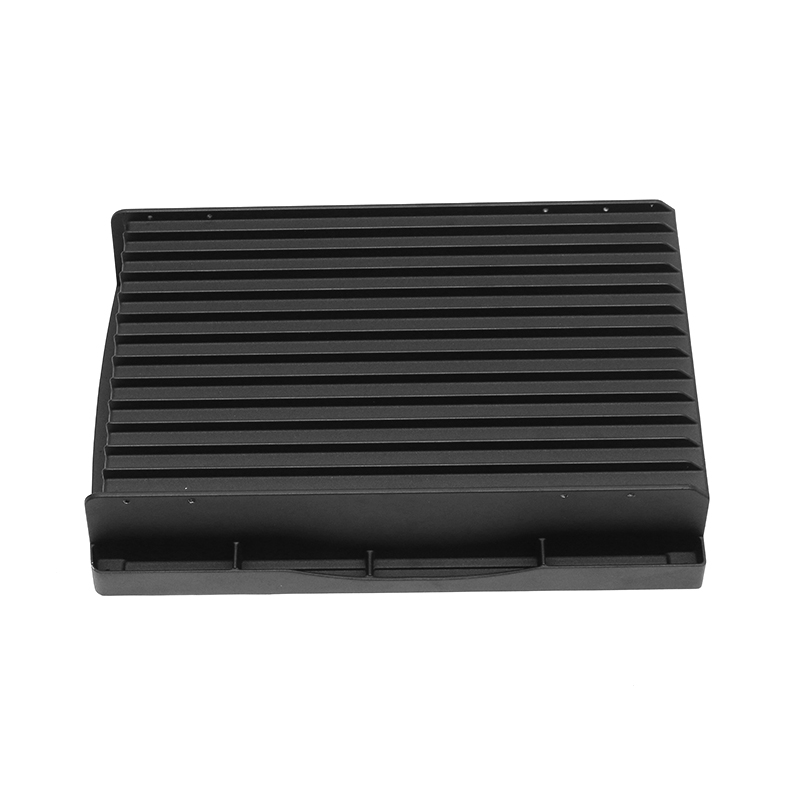
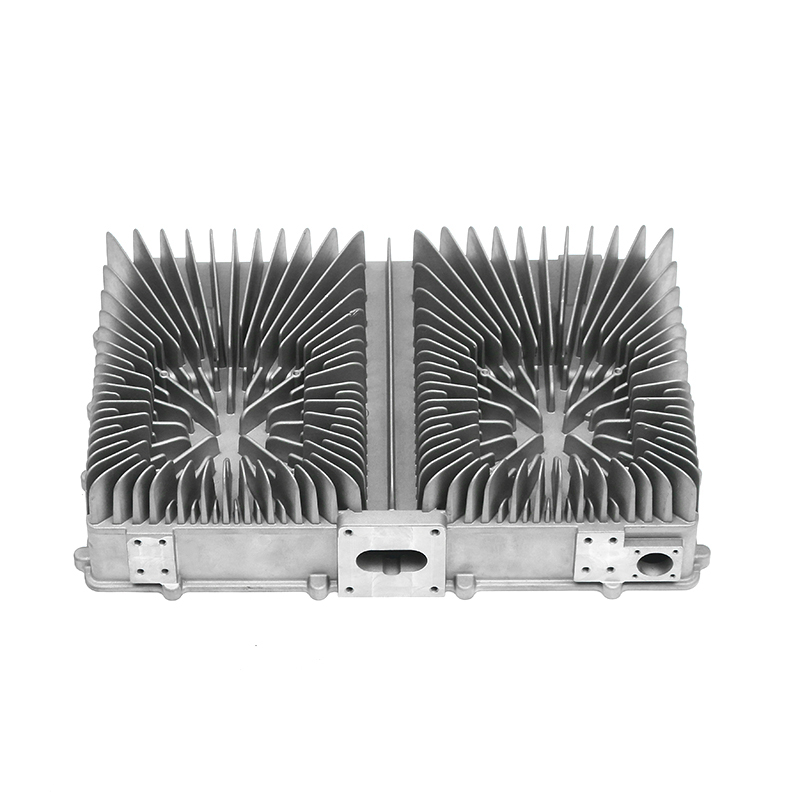
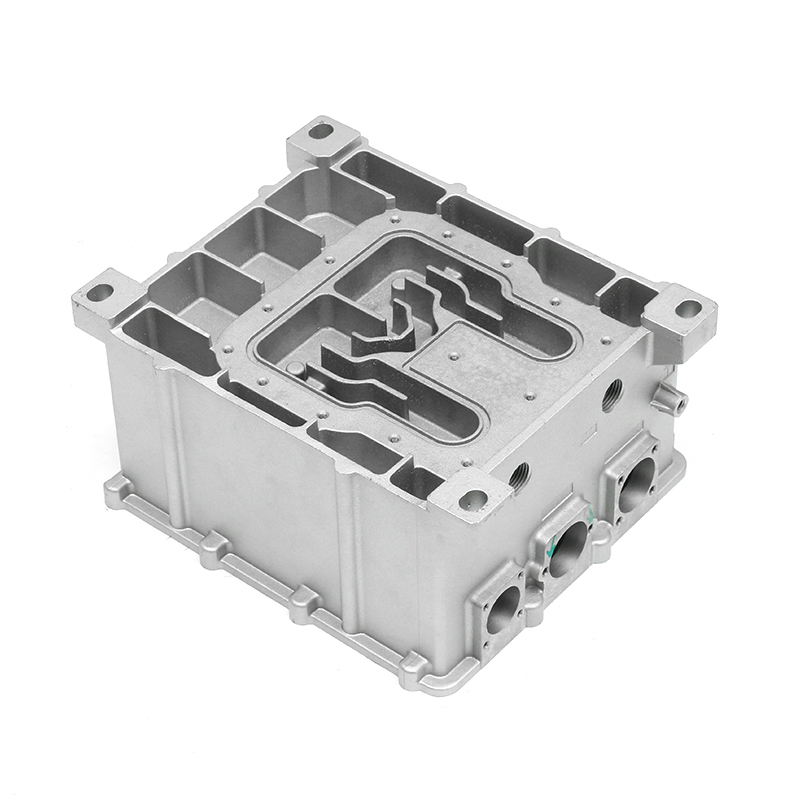
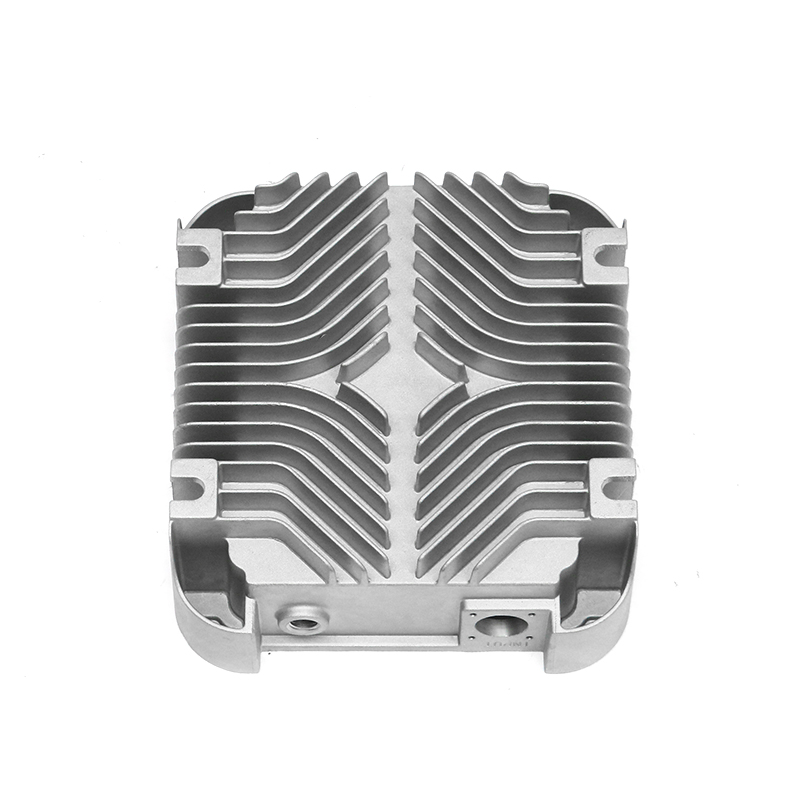
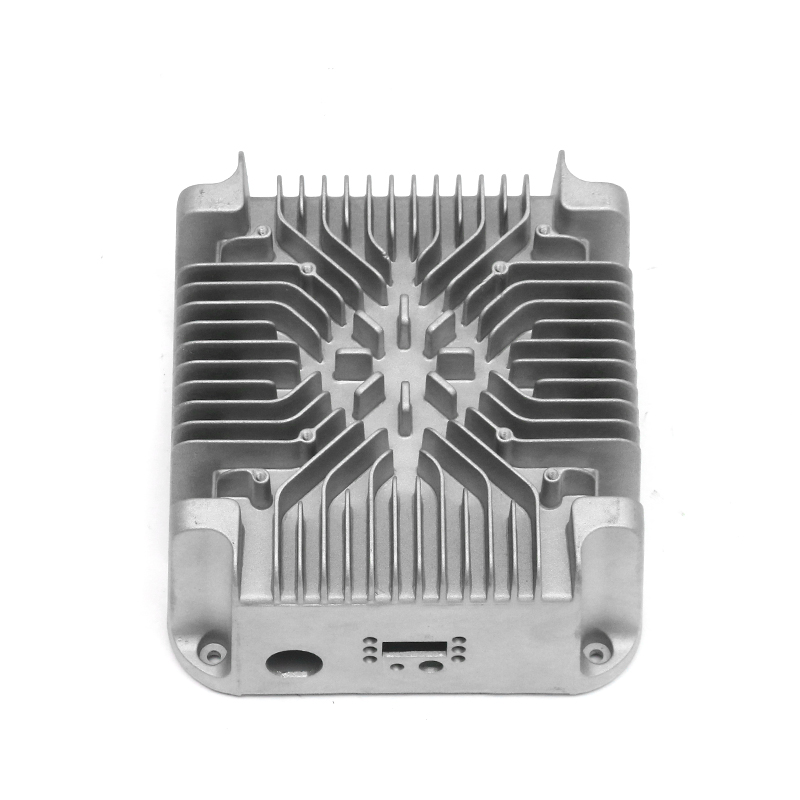
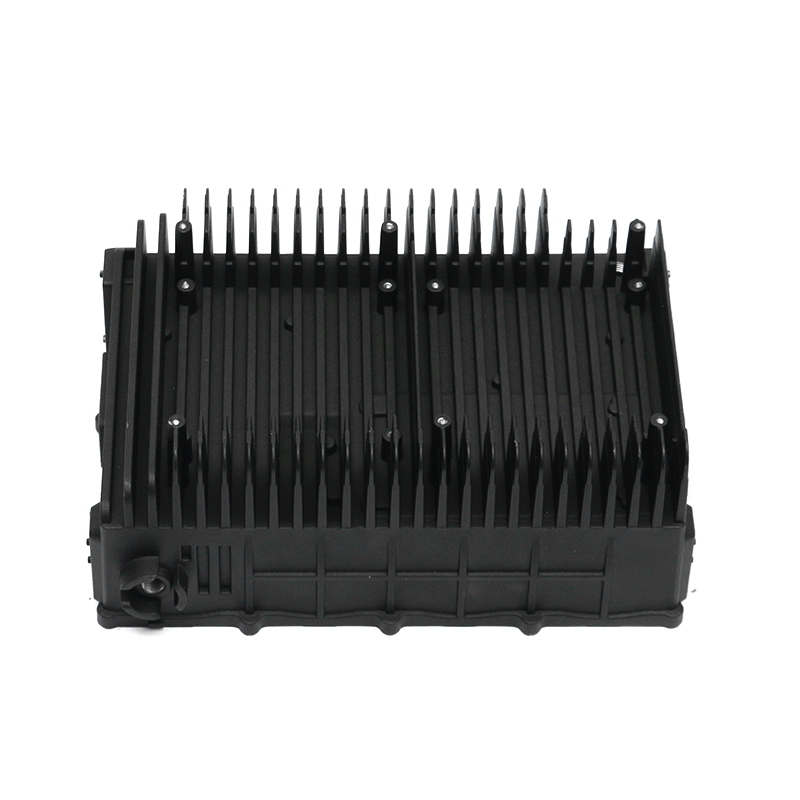
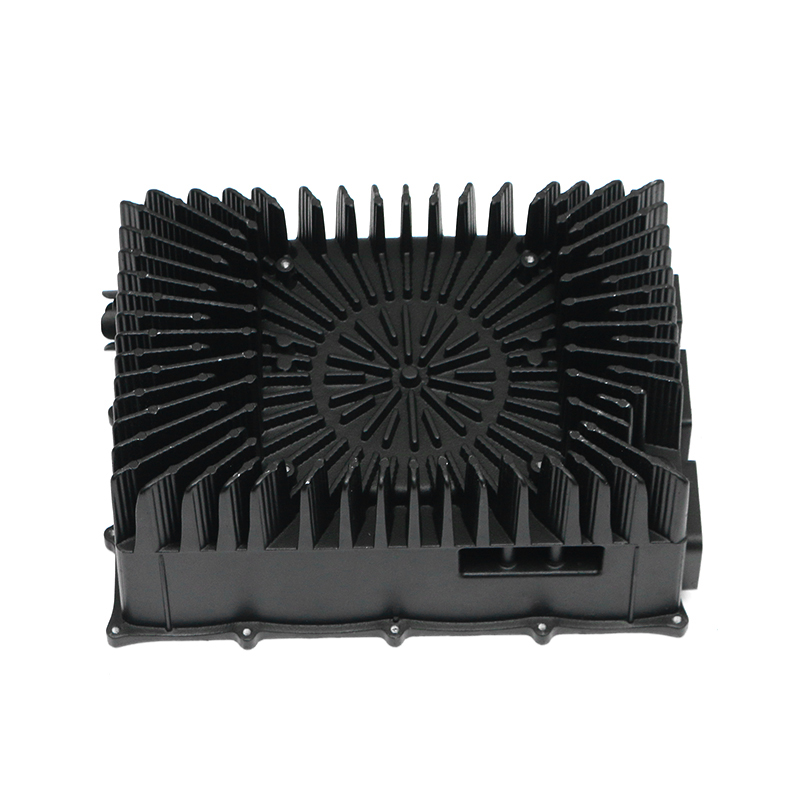
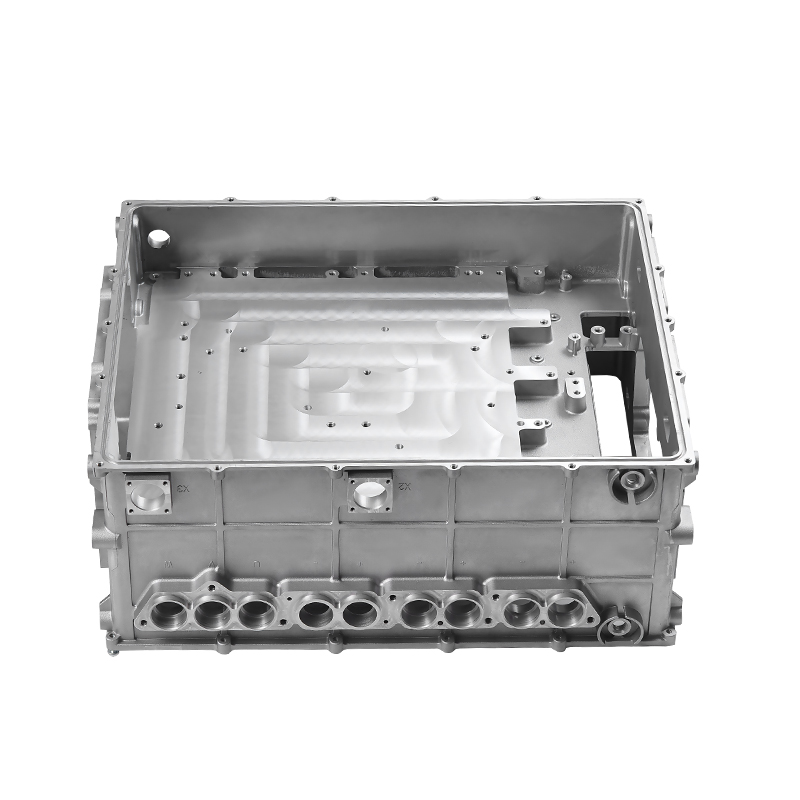
Introduction to Precision Trimming Mold Die Casting
Precision trimming mold die casting is a process commonly used in the manufacturing of metal parts, especially when the products require high levels of detail and complex geometries. Die casting itself is a manufacturing process in which molten metal is injected into a mold cavity under high pressure, producing parts with defined features and high dimensional accuracy. Precision trimming, an essential part of this process, helps remove excess material, clean up the part, and refine its geometry to meet tight specifications. This combination of die casting and trimming plays a crucial role in industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and other sectors where parts often feature intricate designs and stringent performance requirements.
The Role of Precision Trimming in Die Casting
Precision trimming is a secondary operation in die casting that refines the geometry of the product after it has been formed. While die casting itself produces complex geometries, precision trimming focuses on cleaning the part by removing flash, burrs, or other unwanted material that may remain after the casting process. Flash is the excess material that seeps out of the mold cavity during the injection process, and trimming is necessary to ensure that the part conforms to its intended design and function.
The trimming process can involve various techniques such as mechanical cutting, grinding, or electrical discharge machining (EDM), depending on the material and complexity of the part. Precision trimming ensures that the parts not only meet strict dimensional tolerances but also have a smooth surface finish, which is particularly important in industries like electronics, where surface imperfections can affect the performance of the components.
Handling Complex Geometries in Precision Trimming Mold Die Casting
One of the significant advantages of precision trimming mold die casting is its ability to handle products with complex geometries. Die casting is known for its ability to create highly detailed and intricate shapes in a single production step. These geometries can include undercuts, thin walls, deep cavities, and fine features that would be difficult or time-consuming to produce with other manufacturing processes. However, the true challenge comes in ensuring that these complex geometries are preserved and refined during the precision trimming process.
For parts with intricate shapes, the precision trimming process must be carefully controlled to avoid distorting or damaging the part. Advanced trimming techniques and automated machinery are often used to ensure that even the smallest features are accurately trimmed without affecting the overall structural integrity of the part. Precision is particularly critical when dealing with geometries that have tight tolerances or where the part’s function depends on its precise form, such as in the case of injection-molded housings or aerospace components.
Challenges of Handling Complex Geometries
While precision trimming mold die casting is well-suited for complex geometries, the process is not without its challenges. One of the main challenges in trimming parts with intricate features is maintaining the integrity of the delicate structures during the operation. In parts with thin walls or intricate designs, excessive force during trimming can lead to deformations or fractures, which could compromise the part's functionality.
Another challenge is achieving the required surface finish and maintaining dimensional accuracy. Complex geometries often feature sharp corners or small, detailed sections that require high precision. In some cases, manual intervention is necessary to ensure that the trimming process removes the right amount of material while leaving the part in its correct form. Automation and advanced machining technology have improved the precision and repeatability of the trimming process, but human expertise is still needed to handle more complex or delicate parts.
Technological Advances in Precision Trimming for Complex Geometries
Recent technological advances in both die casting and precision trimming have significantly improved the handling of complex geometries. High-speed machining, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) systems, and laser trimming have made it possible to achieve higher precision in less time. With CNC systems, manufacturers can program the trimming process to automatically follow specific paths, making it possible to handle even the most intricate designs with ease. This not only increases efficiency but also reduces the risk of human error, ensuring that each part meets the required specifications.
Laser trimming, which uses focused laser beams to cut and shape the material, is another technology that is becoming more prevalent in the precision trimming process. This method is particularly useful for parts with extremely fine features or where conventional cutting tools might be too large or imprecise. Laser trimming allows for incredibly accurate material removal without physical contact, reducing the risk of damaging the part and providing a high-quality finish.
The Importance of Tooling in Precision Trimming
The quality of the tooling used in precision trimming has a significant impact on how well complex geometries are handled during the casting process. Tooling refers to the molds and machines used to trim, shape, or finish the parts, and it must be designed to withstand the forces and temperatures involved in die casting. Precision trimming molds need to be tailored to each specific product, considering the part's geometry, material properties, and functional requirements.
For highly complex geometries, custom tooling is often necessary to ensure that the trimming process is performed accurately. For example, when working with parts that have undercuts or non-linear shapes, specialized tools such as contour cutters or automated trimming machines may be required to access difficult-to-reach areas. Using the right tooling is essential for maintaining both the quality and the precision of the final product, particularly in industries where even minor defects can lead to performance failures.
Materials Used in Precision Trimming Mold Die Casting
The materials selected for both the die casting process and the precision trimming operation play a crucial role in how well complex geometries can be handled. Metals such as aluminum, zinc, and magnesium alloys are commonly used for die casting due to their fluidity and ability to form intricate shapes with minimal defects. These materials also offer good strength-to-weight ratios, making them ideal for a wide range of applications, including automotive and aerospace industries.
The precision trimming process can be affected by the material's hardness and brittleness. For example, materials like zinc can be easier to trim than harder metals like aluminum or magnesium. Additionally, certain materials may require specific trimming tools or techniques to achieve the desired result without causing damage. Understanding the material's properties is key to selecting the appropriate trimming method and ensuring that the part's geometry is maintained throughout the process.
Comparison of Precision Trimming Techniques for Complex Geometries
| Technique | Benefits | Challenges | Best Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| CNC Machining | High precision, automated process, minimal human error | Expensive equipment, limited by tooling complexity | Parts with high tolerance and intricate designs |
| Laser Trimming | Non-contact, precise material removal, ideal for fine features | Higher cost, may not be suitable for thicker materials | Parts with delicate features or fine details |
| Manual Trimming | Flexibility for unique designs, less investment in equipment | Risk of human error, slower than automated processes | Small batch production or highly specialized parts |
Applications of Precision Trimming Mold Die Casting in Various Industries
Precision trimming mold die casting is widely used across several industries where complex geometries are common. In the automotive industry, for example, parts such as engine components, transmission housings, and brackets often require intricate designs that are efficiently produced through die casting and precision trimming. The ability to produce lightweight yet strong components with complex shapes is crucial for improving fuel efficiency and performance in modern vehicles.
In the aerospace industry, precision die casting is used to create parts that must meet strict performance and safety standards. Complex geometries in aerospace components are often required to minimize weight while maintaining strength and functionality. Precision trimming ensures that these components are manufactured to tight tolerances, reducing the risk of failure during operation.
Electronics is another sector where precision die casting and trimming are critical. Many electronic devices require enclosures, connectors, and other components with fine features and exact specifications. Precision trimming ensures that these parts not only fit properly but also have the necessary surface quality to avoid performance issues related to heat dissipation, electrical conductivity, or mechanical stress.