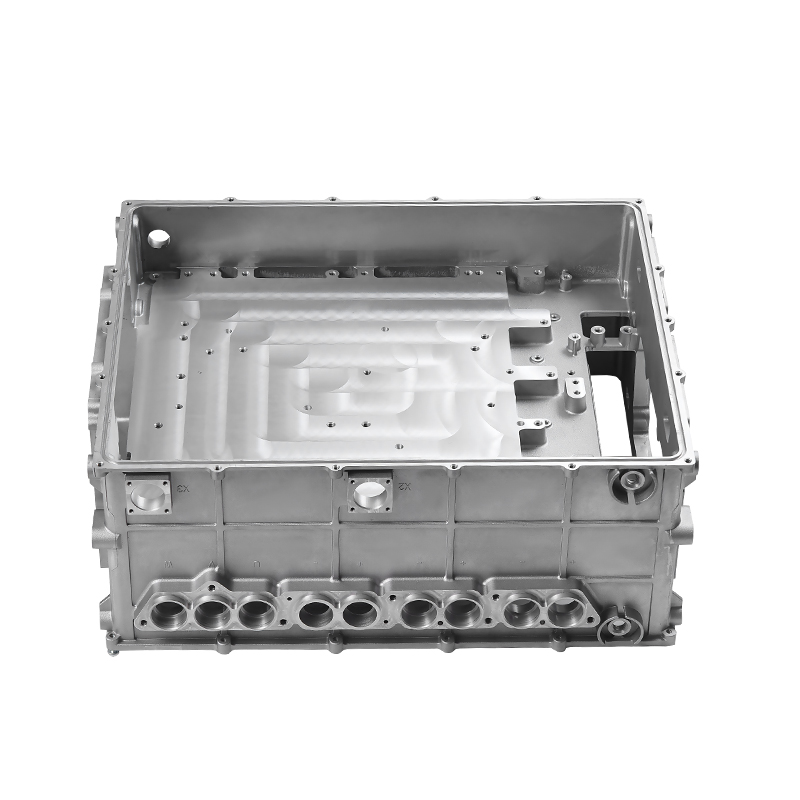
Importance of Sealing Surface and Assembly Datum Accuracy in Car Water Pumps
In automotive cooling systems, the car water pump plays a central role in maintaining stable engine temperature. The accuracy of the sealing surface and the assembly datum directly affects leakage control, bearing life, noise behavior, and overall system reliability. Because modern vehicles operate under continuous vibration, pressure fluctuation, and thermal cycling, even small deviations in these critical areas can lead to sealing failure or misalignment during long-term use.
Die castings are widely used for car water pump housings due to their ability to form complex shapes and integrate multiple functional features. However, die casting also introduces challenges related to dimensional stability, surface flatness, and repeatability. Ensuring accuracy in sealing surfaces and assembly datums therefore requires a coordinated approach that spans mold design, process control, machining, and inspection.
Understanding Sealing Surfaces and Assembly Datums
The sealing surface of a car water pump die casting is the area that interfaces with gaskets, O-rings, or mechanical seals. Its flatness, surface roughness, and positional accuracy determine whether the seal can maintain consistent contact under pressure and temperature changes. Any unevenness may result in localized stress or leakage paths.
Assembly datums are reference features used to locate and align the water pump housing relative to other components such as the engine block, pulley system, or bearing assembly. These datums establish the geometric relationship between critical functional elements. If the datum surfaces or holes are inaccurate, cumulative errors can affect shaft alignment and sealing performance.
Role of Die Casting Mold Design
The foundation of dimensional accuracy begins with mold design. In car water pump die castings, the mold must account for material shrinkage, thermal expansion, and metal flow behavior. Sealing surfaces and datum features are often located in areas of the mold where metal flow is stable and solidification is uniform.
Mold designers incorporate appropriate draft angles, radii, and wall thickness transitions to reduce internal stress and distortion. Critical surfaces are positioned away from areas prone to turbulence or porosity. By controlling these factors at the design stage, the die casting process can produce near-net-shape parts with consistent geometry.
Control of Aluminum Alloy and Melt Quality
The choice of aluminum alloy influences both castability and dimensional stability. Alloys commonly used for car water pump housings are selected for their balance of strength, thermal conductivity, and resistance to deformation. Consistent alloy composition helps ensure predictable shrinkage behavior during solidification.
Melt quality control is equally important. Degassing, temperature regulation, and impurity management reduce the risk of internal defects that could affect surface accuracy. A stable melt condition allows the metal to fill sealing surface regions evenly, reducing the need for excessive post-casting correction.
Process Parameters in Die Casting Production
Injection speed, pressure, and cooling time have a direct impact on the final dimensions of a die casting. Excessive injection speed may cause turbulence, while insufficient pressure can lead to incomplete filling of fine features. Both scenarios can affect sealing surfaces and datum locations.
Cooling rate is carefully managed to minimize uneven contraction. Uniform cooling across the mold reduces warpage and helps maintain flatness in sealing areas. Process consistency from shot to shot ensures that dimensional variation remains within acceptable limits.
Post-Casting Stress Relief and Stabilization
Residual stress is an inherent characteristic of die cast parts. These stresses may be released gradually during machining or service, potentially altering critical dimensions. To address this, some car water pump die castings undergo stabilization treatments such as controlled aging or thermal conditioning.
These treatments allow internal stresses to redistribute in a controlled manner before final machining. As a result, sealing surfaces and assembly datums remain more stable over time, improving the reliability of subsequent machining operations.
Precision Machining of Sealing Surfaces
Although die casting can achieve relatively tight tolerances, sealing surfaces typically require precision machining to meet flatness and surface roughness requirements. CNC machining centers are used to mill or grind these surfaces using defined tool paths and cutting parameters.
The machining process references predefined datums to ensure consistency. Tool wear, cutting speed, and fixture rigidity are closely monitored to prevent deviations. This controlled approach ensures that the sealing surface meets the requirements of gasket compression and long-term sealing behavior.
Establishing Reliable Assembly Datums
Assembly datums are often created or refined during machining rather than relying solely on as-cast features. Machined reference planes, bores, or holes provide accurate and repeatable alignment points for assembly.
By defining a clear datum hierarchy, manufacturers ensure that all subsequent machining operations relate back to the same reference system. This reduces cumulative error and maintains the positional relationship between sealing surfaces, shaft bores, and mounting interfaces.
Fixture Design and Positioning Accuracy
Machining fixtures play a critical role in preserving accuracy. Fixtures must locate the die casting securely without inducing distortion. Contact points are carefully chosen to support the part while avoiding deformation of sealing surfaces.
Repeatable fixture positioning ensures that each part is machined in the same orientation. This consistency is essential for maintaining uniformity across large production volumes of car water pump die castings.
Surface Flatness and Roughness Control
Flatness and surface roughness are key parameters for sealing surfaces. Flatness ensures uniform gasket compression, while appropriate roughness promotes sealing without damaging the gasket material. Machining strategies are selected to balance these requirements.
Finishing operations may include fine milling or light grinding. Tool selection and feed rates are optimized to achieve the desired surface characteristics while maintaining dimensional accuracy.
Dimensional Inspection and Measurement Techniques
Inspection is essential to verify that sealing surfaces and assembly datums meet design specifications. Coordinate measuring machines are commonly used to measure flatness, parallelism, and positional accuracy. These measurements provide quantitative data that can be traced back to specific process parameters.
Surface roughness testers are used to confirm that sealing surfaces fall within acceptable ranges. Regular inspection allows manufacturers to detect trends and make timely adjustments to tooling or machining processes.
Use of Statistical Process Control
Statistical process control helps maintain consistency in high-volume production. By monitoring key dimensions related to sealing surfaces and datums, manufacturers can identify variations before they lead to out-of-tolerance parts.
Control charts and process capability analysis provide insight into long-term stability. This data-driven approach supports continuous improvement and reduces the likelihood of assembly issues in downstream processes.
Typical Accuracy Targets for Key Features
The following table illustrates typical accuracy targets for sealing surfaces and assembly datums in car water pump die castings. Actual requirements vary depending on pump design and application.
| Feature Type | Typical Accuracy Requirement | Functional Purpose |
| Sealing surface flatness | Tight flatness tolerance | Ensure uniform gasket compression |
| Surface roughness | Controlled fine roughness | Support stable sealing performance |
| Assembly datum position | Precise positional tolerance | Maintain alignment with engine block |
Managing Porosity and Its Effect on Accuracy
Internal porosity can influence machining accuracy if voids intersect critical surfaces. Process optimization in die casting reduces porosity levels, particularly near sealing and datum areas. X-ray inspection or other non-destructive methods may be used to assess internal quality.
By controlling porosity, manufacturers reduce the risk of surface collapse during machining and maintain consistent dimensional results.
Coordination Between Design and Manufacturing Teams
Ensuring accuracy is not solely a manufacturing task. Design engineers specify tolerances, sealing concepts, and datum schemes that align with die casting and machining capabilities. Early collaboration helps avoid designs that are difficult to produce consistently.
Feedback from production and quality teams informs design adjustments, leading to more robust car water pump die castings that meet functional requirements without excessive manufacturing complexity.
Influence of Thermal Expansion During Operation
Sealing surfaces and assembly datums must remain effective not only at room temperature but also under operating conditions. Aluminum die castings expand with heat, and this expansion must be predictable and uniform.
Accurate machining and consistent material properties ensure that thermal expansion does not compromise sealing or alignment. This consideration reinforces the importance of accuracy throughout the manufacturing process.
Continuous Improvement Through Process Feedback
Manufacturers rely on feedback from assembly lines and field performance to refine accuracy control methods. If leakage or alignment issues are observed, root cause analysis may trace the problem back to specific casting or machining steps.
This continuous improvement loop helps maintain reliable sealing surface and assembly datum accuracy over the lifecycle of the product and across successive production batches.